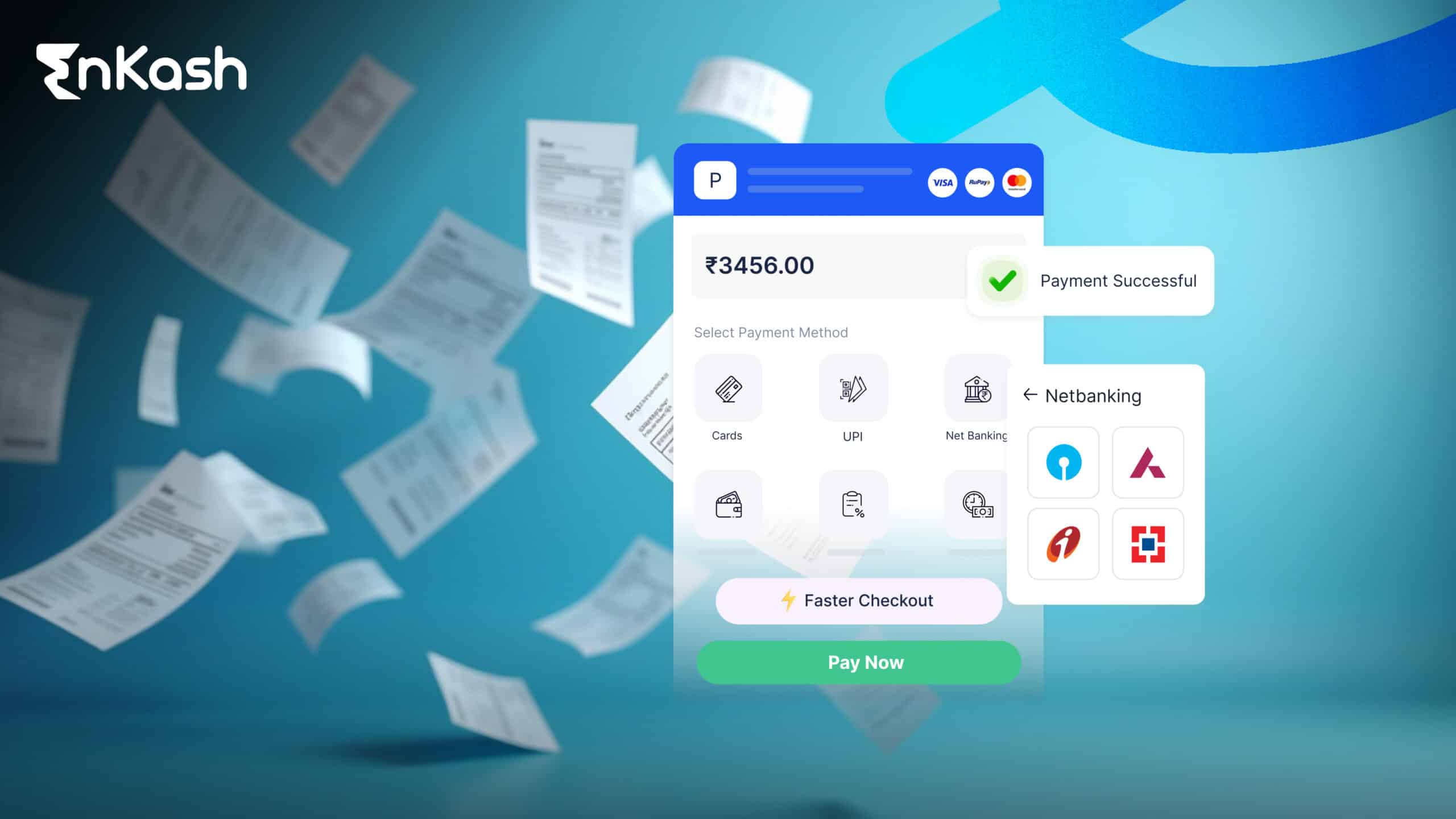
Payment gateways are called ‘gateways’ because they create secure communication links between customers, merchants, and banks during online transactions. Similar to how physical toll gates check vehicles before entry, payment gateways authenticate payment information before allowing fund transfers. From selecting the payment method to payment completion, the entire process happens in seconds. Let’s find out more about payment gateways below.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway serves as the technological system that enables online transactions between customers and merchants by acting as an intermediary. The payment gateway encrypts sensitive financial information, which protects payments from fraud while maintaining transaction security.
Importance of Payment Gateways in Online Transactions
As online shopping and digital services rapidly expand, payment gateways have become essential for modern commerce. Payment gateways allow companies to receive money through credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and UPI, and some also support cryptocurrency transactions, depending on the gateway and region. They serve beyond payment processing functions by building user trust through encryption and multi-factor authentication alongside fraud detection measures.
The Evolution of Payment Gateways
Payment systems have evolved significantly from basic cash exchanges to cheques and credit cards before reaching today’s digital payment methods. The internet revolutionized shopping by establishing online payments as an essential requirement. Payment gateways support digital transactions through the smooth integration of banks with customers and merchants.
Bridging the Gap Between Customers and Merchants
Payment gateways work as intermediaries for online transactions by securely transferring data between customers, merchants, and financial institutions. Before sending money to the merchant’s account, the system confirms payment authentication and checks available funds. Customers would lose their secure online shopping options, and businesses would struggle with intricate financial procedures in the absence of payment gateways.
Read More: Payment Links
How a Payment Gateway Works
Payment gateways function invisibly to provide fast and secure online transaction processing with seamless user experiences.
Transaction Flow: Step-by-Step Guide
This step-by-step guide explains the payment gateway process.
- Customer Initiates a Transaction
The customer initiates an online transaction by selecting their desired product or service and moving forward to the checkout page. The customer selects their payment method, including options like credit/debit card, net banking, UPI, or a digital wallet.
- Payment Details are Encrypted
When customers submit payment information to a payment gateway, it uses Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or TLS encryption to protect their data from unauthorized access. Customers’ sensitive data, like card numbers and UPI IDs, remain shielded against cyber threats through this protective measure.
- The Payment Gateway Sends Details to the Acquiring Bank
The payment gateway securely sends encrypted payment information to the acquiring bank, which handles the merchant’s transaction processing.
- Bank Communicates with Payment Networks (Visa/Mastercard/UPI)
Following receipt of the transaction request from the payment gateway, the acquiring bank sends it to the appropriate payment networks like Visa, Mastercard, RuPay, and UPI. Payment networks (Visa/Mastercard/UPI) function as intermediaries between the acquiring bank and the issuing bank (customer’s bank).
- Issuing Bank Authorizes or Declines
The issuing bank (which serves as the customer’s bank) verifies the transaction through a validation process.
- Whether the card or account is valid
- The issuing bank checks if the customer’s account holds adequate funds or credit.
- Any security flags for fraudulent activity
- After evaluating the transaction information, the issuing bank decides to either approve or decline the payment request
- Merchant Receives Confirmation
The merchant receives payment gateway notification and processes payment upon transaction approval. A confirmation message reaches the customer before the funds reach the merchant’s account within a timeframe of hours to days.
Key Components of a Payment Gateway
Multiple essential participants collaborate within the payment gateway ecosystem.
- Customer: The person initiating the online transaction.
- Merchant: Goods and services sellers consist of businesses and individuals.
- Payment Gateway: The payment gateway technology handles both the encryption and processing of transactions.
- Acquiring Bank: The acquiring bank functions as the financial institution where merchants receive their payments.
- Issuing Bank: The financial institution that offers the customer their payment card or UPI service functions as the issuing bank.
- Payment Processor: Payment processors handle requests and approve transactions while transferring funds between banks.
Read more: What is the Difference Between a Payment Gateway and a Payment Processor
Security Measures in Payment Gateways
Payment gateways place the utmost importance on security because online transactions continue to grow. A range of security measures protect customer data against cyber threats and fraudulent activities.
- Encryption
SSL/TLS encryption allows payment gateways to secure payment information by encoding it so that customer data remains encrypted during transmission.
- Tokenization
Payment gateways protect sensitive card information using tokenization, which replaces real card details with a randomly generated token that has no usable value for hackers. The token provides additional protection since its inception does not lead to any usable data.
- Fraud Prevention Mechanisms
- The AI-driven fraud detection system analyzes user spending patterns to pinpoint suspicious activity.
- 3D Secure authentication (OTP or biometric verification)
- Risk scoring functions by marking high-risk transactions that require additional investigation.
- PCI DSS Compliance
Payment gateways operate under Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) regulations that enforce security protocols for the processing and storing of payment data.
Types of Payment Gateways
The following sections explain the main categories of payment gateways.
1. Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted payment gateways send customers to an external payment service provider’s page to finalize their transactions. The gateway manages payment processing and ensures security and compliance, which lightens the merchant’s workload.
Advantages
- Easy integration with websites and apps
- The hosted payment gateway provider takes care of security compliance requirements.
- Trusted by customers due to established brands
Disadvantages
- The redirection of customers to another website during payment processing can lead to potential disruptions in user experience.
- Limited customization options for merchants
Examples of Hosted Payment Gateways
- The UPI Payment Gateway enables customers to perform instant bank-to-bank transfers using UPI technology.
- Paytm Payment Gateway provides smooth transaction processing for UPI, wallet payments, and credit/debit cards.
- Razorpay Payment Gateway is the most secure and popular payment solution for Indian businesses.
- The Stripe Payment Gateway is the preferred choice for international online businesses.
2. Self-Hosted Payment Gateways
Self-hosted payment gateways enable businesses to collect payment data on their platforms and handle transactions through their servers. Self-hosted payment gateways enable merchants to handle their payment processes, which gives large businesses the necessary flexibility to create customized payment experiences.
Advantages
- Full control over the payment process
- Enhanced customization for branding and user experience
- Direct integration with business analytics
Disadvantages
- Businesses need to implement advanced security protocols that include PCI DSS compliance.
- Increased responsibility for fraud detection and prevention
- More complex setup and maintenance
Who Uses Self-Hosted Payment Gateways?
- Large enterprises with dedicated IT teams
- Businesses that prioritize customer experience and branding
- Companies dealing with high transaction volumes
3. API-Based Payment Gateways
Businesses can embed payment processing functions into their websites or applications through the use of an Application Programming Interface (API) with API-based payment gateways. API gateways maintain customer interaction within the same webpage throughout checkout, unlike hosted gateways, which provide an uninterrupted user experience.
Advantages
- Fully customizable checkout experience
- By staying on the merchant’s site during transactions, customers develop greater trust.
- Can integrate with multiple payment methods
Disadvantages
- Requires technical expertise for integration
- PCI DSS compliance and security fall under the responsibility of business organizations.
Examples of API-Based Payment Gateways
- Razorpay Payment Gateway – Popular for Indian businesses
- PayU Payment Gateway delivers functionality for multi-currency transactions along with subscription payment options.
- Stripe Payment Gateway offers developer-friendly APIs, making it suitable for global businesses.
- The Cashfree Payment Gateway enables immediate payment processing and link generation for transactions.
Read More: Bulk Collect
4. Bank Payment Gateways
Banks offer direct payment processing solutions called payment gateways for businesses to handle online transactions. Large enterprises and businesses needing direct bank account settlements tend to choose these gateways.
Advantages
- Direct integration with banking services
- The bank manages transactions, which enhances payment processing security.
- This payment solution fits organizations that need to handle high volumes of transactions.
Disadvantages
- The initial setup requires extensive verification and approval procedures.
- Limited flexibility compared to third-party payment gateways
- The service lacks support for contemporary payment options such as digital wallets and Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
Examples of Bank Payment Gateways
- The State Bank of India endorses SBI Payment Gateway as its trusted payment solution.
- HDFC Payment Gateway – Offers advanced fraud protection
- ICICI Payment Gateway enables smooth integration with business banking systems.
- The Tata Capital Payment Gateway provides a secure platform for executing large financial transactions.
5. International Payment Gateways
International payment gateways give global businesses the ability to process multi-currency transactions across borders while meeting international payment regulations. E-commerce platforms serving global customers depend on these gateways to process transactions effectively.
Advantages
- Supports multiple currencies and global transactions
- Complies with international payment security standards
- International payment gateways enable businesses to process payments from customers around the world.
Disadvantages
- Higher transaction fees due to currency conversion
- Compliance requirements vary across regions
- International transactions may involve additional processing time
Examples of International Payment Gateways
- Stripe Payment Gateway is a popular choice for businesses conducting international payment transactions.
- PayPal Payment Gateway has earned its reputation as one of the most dependable global payment systems.
- The ICEGATE Payment Gateway serves as a tool for processing transactions related to international trade and customs clearance.
- Razorpay Payment Solutions for India provides international payment services designed specifically for Indian businesses.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Aggregator
Payment gateways and payment aggregators serve vital functions within digital transactions to enable smooth online payment experiences. Although they appear alike, payment gateways and payment aggregators operate differently to meet distinct business requirements.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a secure technology platform that manages online transactions by transferring payment data between the customer and merchant and the acquiring and issuing banks. Payment gateways are secure connections between merchants’ websites and financial institutions while encrypting and authorizing transactions.
How It Works
- The customer enters payment details at checkout.
- The payment gateway uses encryption to send payment details to the acquiring bank.
- The bank sends payment requests through Visa, Mastercard and UPI payment networks for processing.
- The bank approves or declines the transaction request.
- The payment gateway sends transaction results to both the merchant and the customer.
Examples are EnKash, Razorpay, PayU, CCAvenue, Stripe, PayPal, etc.
What is a Payment Aggregator?
A payment aggregator provides a service that allows multiple merchants to process online payments without needing separate merchant accounts at banks. The payment aggregator receives payments for businesses and handles the subsequent transaction settlement process.
How It Works
- Businesses use one payment aggregator for registration because it eliminates the need for multiple banking institution accounts.
- The aggregator gathers customer payments for numerous merchants.
- After processing, the collected payments are settled into accounts belonging to each merchant.
Examples are EnKash, PhonePe, Paytm, Razorpay, Easebuzz
Key Differences: Payment Gateway vs. Payment Aggregator
Feature |
Payment Gateway |
Payment Aggregator |
Definition |
A technology that securely transmits payment information between merchants and banks |
A service provider that collects and processes payments on behalf of multiple merchants |
Merchant Account Requirement |
Merchants need to open an individual merchant account with an acquiring bank. |
Merchants do not need their own merchant account; they operate under the aggregator’s account |
Operational Model |
Acts as a link between the merchant, acquiring bank, and issuing bank. |
Acts as an intermediary that pools transactions from multiple merchants. |
Technical Setup |
Requires direct integration with merchant websites. |
Provides simpler integration for businesses by handling banking relationships. |
Regulatory Compliance |
Merchants need to comply with PCI DSS and banking regulations individually. |
The aggregator handles compliance and security for multiple merchants. |
Best Suited For |
Large businesses that require full control over payment processing |
Small to medium-sized businesses that want a quick and hassle-free payment solution. |
Examples of Payment Aggregators in India
- EnKash Payment Gateway: Supports 100+ payment options while offering developer friendly integrations and secure and compliant platform
- PhonePe Payment Gateway: Supports UPI, credit/debit cards, and wallets.
- Paytm Payment Gateway: The platform delivers quick payment settlements along with numerous payment options.
- Razorpay Payment Gateway: Provides seamless API integration for businesses.
- Easebuzz Payment Gateway: This payment gateway delivers simple startup and small business onboarding processes.
Read More: e-Nach
Importance of Payment Gateways for Businesses
Payment gateways now serve as critical infrastructure for businesses because cash transactions are diminishing in the modern digital environment. A secure and reliable payment gateway helps improve customer experience while boosting conversions and generating revenue growth.
Why Every Business Needs a Payment Gateway
Here’s why every business—small or large—needs a payment gateway.
- Payment gateways protect sensitive payment data through encryption, which prevents fraud and ensures secure transaction processing.
- The payment gateway enables customers to complete transactions through credit/debit cards along with UPI, net banking options, digital wallets, plus additional international payment methods.
- Online payment gateways power businesses to process payments at all hours of the day.
- Businesses can connect payment gateways with their websites or mobile applications, and also offline point-of-sale systems.
How Payment Gateways Enhance Customer Experience
Here’s how payment gateways improve user experience.
- Payment gateways deliver quick transaction processing in seconds to eliminate extended wait periods.
- Securely stored payment information enables returning customers to complete future transactions with ease through one-click payments and auto-save features.
- International businesses receive payments from global customers directly without having conversion obstacles.
Role of Payment Gateways in E-Commerce & Websites
Here’s why E-commerce sites and service-based websites must implement a payment gateway.
- A well-integrated payment gateway creates a smooth checkout process that delivers the fast and straightforward payment experience customers demand.
- Lengthy and complex payment procedures tend to lead customers to abandon their shopping carts. Payment gateways make transactions easier, which leads to more completed purchases.
- Subscription-based businesses, including streaming services and SaaS platforms, use payment gateways to manage automated billing and renewal processes.
Impact of Payment Gateways on Conversion Rates & Revenue
A dependable and intuitive payment gateway positively affects transaction conversion rates alongside total revenue earned by businesses. Here’s how.
- Customers complete their purchases more frequently when payment processes run smoothly, which results in fewer abandoned transactions.
- Secure payment gateways that customers recognize help assure them about the safety of their financial information.
- Different payment methods, such as EMI options and digital wallets, expand customer reach and enhance sales performance.
Top Payment Gateways in India
This section explores the selection criteria for payment gateways and reviews the top 10 payment gateways available in India.
Criteria for Selecting the Best Payment Gateway in India
Several factors need to be considered when deciding which payment gateway to use.
- Transaction Fees and Pricing: Analyze the initial setup fees together with transaction costs and any concealed charges.
- Payment Methods Supported: The payment gateway needs the functionality to support payments through credit/debit cards as well as UPI, net banking, and digital wallets.
- Integration and Compatibility: Your website or app needs to connect fast to your existing systems and confirm compatibility.
- Settlement Period: Determine the time frame required for deposits to reach your account from payments.
- Security Features: Choose payment gateways that meet PCI DSS standards and have built-in fraud detection capabilities.
- Customer Support: Prompt support from reliable sources helps resolve problems quickly, which reduces operational disruptions.
Detailed Overview of the Top 10 Payment Gateways in India
This section presents a detailed examination of the ten best payment gateways available in India.
1. Razorpay Payment Gateway
Features
- Comprehensive Payment Options: The Razorpay payment gateway allows transactions through credit/debit cards as well as UPI, net banking options, and e-wallet services.
- Developer-Friendly: Provides broad API access and complete documentation to enable smooth integration processes.
- Dashboard Analytics: Provides real-time insights into transactions and settlements.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: This payment gateway charges a fee of 2% per transaction on Indian cards and UPI, but the fee is 3% for international cards and Amex.
- No Setup or Annual Maintenance Charges.
Integration
Major platforms, including Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento have available integration plugins.
2. Paytm Payment Gateway
Features
- UPI-Based Transactions: Facilitates quick and secure UPI payments.
- Wide Acceptance: The payment gateway supports various payment solutions such as Paytm Wallet, bank cards, and net banking options.
- Instant Settlements: The service provides instant fund transfers directly into the merchant’s account.
Pricing
There is no initial setup fee and the transaction fee varies depending on the payment method used.
Integration
APIs and SDKs offer easy integration across multiple platforms with user-friendly interfaces.
3. EnKash Payment Gateway
Features
- Comprehensive Payment Options: EnKash supports 100+ payment methods, including net banking, UPI, digital wallets, and credit/debit cards, providing customers with multiple choices for payment.
- Developer-Friendly: Offers robust SDKs, APIs, and plugins to ensure smooth integration, complete documentation, and a secure sandbox environment, making it easy for developers to set up.
- Enhanced Checkout Experience: Facilitates frictionless payments with secure global card saving and personalized payment options for a seamless customer experience.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: EnKash charges a competitive transaction fee, which varies based on the payment method. While specific fee details are generally provided on request, the service typically offers cost-effective pricing for high-volume businesses.
Integration
- EnKash integrates seamlessly with major e-commerce platforms such as Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento. It also supports various accounting and CRM platforms, providing broad flexibility for businesses in diverse industries.
4. PhonePe Payment Gateway
Features
- Extensive User Base: Uses PhonePe’s popularity for widespread acceptance.
- Multiple Payment Options: Supports UPI, cards, and wallets.
- Secure Transactions: Deploys strong security protocols to secure user information.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: Competitive rates; specific details available upon inquiry.
- No Setup or Annual Maintenance Charges.
Integration
Simple integration process with comprehensive developer support.
5. Stripe Payment Gateway
Features
- International Payments: Businesses can process payments from customers across the globe using this feature.
- Advanced Security: Incorporates fraud prevention tools and encryption standards.
- Customizable Checkout: The system allows businesses to customize their checkout experience to reflect their brand’s visual style.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: A fee of 2.9% plus ₹7 applies to each successful card transaction along with extra charges for currency conversion.
- No Setup or Monthly Fees.
Integration
The platform offers APIs alongside ready-made solutions with multiple platforms and programming languages.
6. CCAvenue Payment Gateway
Features
Multi-Bank Processing: Works alongside multiple banking institutions to maintain high success rates.
Extensive Payment Options: Supports cards, net banking, UPI, and wallets.
Multi-Currency Support: The payment system accepts multiple currencies which helps global businesses manage international transactions.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: Each transaction will incur fees between 2% to 3%, which vary according to the selected plan.
- Setup Fee: Applicable; varies based on the chosen plan.
Integration
Delivers plugins to work with major e-commerce platforms and APIs for specialized integration development.
7. Cashfree Payment Gateway
Features
- Fast Settlements: Offers same-day settlement options, enhancing cash flow.
- Comprehensive API Suite: Facilitates easy integration and customization.
- Wide Payment Acceptance: The system accepts more than 100 payment methods which cover cards as well as UPI and wallet options.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: The popular payment methods incur a transaction fee of 1.95% while other methods have variable fees.
- No Setup or Annual Maintenance Charges.
Integration
Developer-friendly with extensive documentation and SDKs.
8. Instamojo Payment Gateway
Features
- Ideal for Small Businesses: This payment gateway solution allows startups and SMEs to get started with little documentation.
- Digital Product Support: The payment gateway supports secure transactions for digital goods sales.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies payment collection through links and buttons.
Pricing
Transaction Fees: 2% + ₹3 per transaction.
No Setup or Annual Maintenance Charges.
Integration
Websites and blogs, along with social media apps, can easily link with the system.
9. PayU Payment Gateway
Features
- Global Transactions: Enables businesses to reach international markets by providing international payment solutions.
- Customizable Solutions: Provides personalized payment options that accommodate different business structures.
- Robust Security: Implements advanced fraud detection and prevention mechanisms.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: Standard transaction fees stand at approximately 2% but may differ according to the volume of business transactions and the business type.
- Setup and Maintenance: Businesses will not encounter setup fees but annual maintenance fees will depend on the selected plan.
Integration
The system integrates effortlessly with top e-commerce platforms while supplying full-featured APIs for tailor-made solutions.
10. BillDesk Payment Gateway
Features
- Trusted by Government Organizations: Governmental services frequently depend on this platform to handle payment transactions.
- High Reliability: Ensures consistent uptime and dependable transaction processing.
- Comprehensive Payment Options: The service accepts multiple payment methods from cards and net banking to UPI.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: Transaction fees usually fall between 1.5% and 2.5%, but these rates can be adjusted through negotiation.
- Setup Fees: Setup fees might exist with further details available through direct requests for information.
Integration
The platform provides APIs and integration support with multiple platforms for business adaptability.
11. Easebuzz Payment Gateway
Features
- Emerging Platform for Small Businesses: Provides scalable payment solutions tailored for startups and small to medium enterprises.
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform makes payment collection simple through easy-to-use tools.
- Multiple Payment Modes: The payment gateway system can process transactions through cards along with UPI, net banking options, and digital wallets.
Pricing
- Transaction Fees: Transaction fees begin at 2% with competitive rates while final fees depend on the selected services.
- Setup and Maintenance: Small businesses find the service cost-effective because it requires no setup fees, only minimal maintenance fees.
Integration
The system allows simple integration into leading e-commerce platforms while providing APIs to meet bespoke needs.
Read More: Payment Page
Payment Gateway Integration Process
The integration process uses a systematic method regardless of your choice between a custom website and a Shopify platform to ensure smooth transactions.
Steps to Integrate a Payment Gateway on a Website
1. Select the Right Payment Gateway
The choice of a payment gateway depends heavily on transaction fees, supported payment methods, security measures, and how easily it integrates. Some of the top choices include.
- Startups and Indian businesses find Razorpay optimal for its effortless API integration capability.
- Stripe serves businesses that require payment processing across multiple international markets.
- PayU serves global transactions and enterprise-level companies.
- Paytm – Popular for UPI-based transactions in India.
- CCAvenue delivers multi-bank processing abilities along with extensive payment method support.
2. Register as a Merchant
The business must complete the merchant registration process on the selected payment gateway’s platform. This process typically includes.
- All required business information, including the company name and bank account details, along with the website URL, needs to be delivered for registration.
- Businesses need to submit required verification documents including GST details, PAN card, and bank statements.
- The business must agree to the payment gateway’s terms and conditions.
- The merchant gains access to both the gateway’s API and dashboard following the approval process.
3. API Integration & Plugin Setup
Payment gateways provide various integration solutions that depend on how your website is configured.
API Integration: Custom website businesses must incorporate their payment gateway’s API into their backend system. This involves:
- Installing the Software Development Kits that come from the payment gateway.
- Configuring endpoints for payment processing.
- Develop server-side scripts to process transaction requests and send appropriate responses.
Plugin Integration: Companies using CMS platforms such as WordPress (WooCommerce), Magento, or PrestaShop can install pre-built plugins provided by their payment gateway. Minimal coding enables businesses to simplify the integration process with available plugins and SDKs.
4. Payment Testing
Prior to launching, businesses need to perform transaction tests to verify the correct gateway operation. Developers can use sandbox mode within the payment gateway to conduct payment simulations that do not involve real money transfers. Testing ensures the following.
- Transactions are successfully processed.
- Error handling mechanisms work properly.
- The payment gateway security mechanisms, including encryption and tokenization, operate according to specifications.
5. Go Live and Monitor Transactions
After completing successful tests, the payment gateway is ready for live mode. Businesses need to use the payment gateway’s dashboard to continuously monitor transactions, which helps them track payment activities and identify failed transactions, while preventing fraud.
Payment Gateway Integration for Shopify & E-Commerce Stores
Integrating a payment gateway with Shopify and other e-commerce platforms proves to be a simple process.
- Businesses have access to Shopify Payments from Shopify itself as their native gateway option while simultaneously being able to integrate third-party gateways such as Razorpay, PayU, CCAvenue or Atom Payment Gateway.
- Several payment gateways deliver pre-built Shopify applications with limited configuration requirements.
- Merchants must input their API keys and set up their preferences through the Shopify dashboard.
Payment Gateway Charges & Cost Structure
This section delves into the different charges associated with payment gateways, compares fees among leading providers, and explores the availability of free options.
Breakdown of Charges in Payment Gateways
Payment gateways usually charge multiple types of fees including setup fees and transaction fees.
- Setup Fees: Setup fees are a singular cost for starting payment gateway configuration and integration.
- Transaction Fees: Payment gateways take a percentage fee from every transaction they handle.
- Maintenance Fees: Payment gateways usually require annual recurring charges to maintain and support their services.
Comparison of Charges for Leading Payment Gateways
Here is a detailed comparison of charges for different payment gateways.
Payment Gateway |
Setup Fees |
Transaction Fees |
Maintenance Fees |
Razorpay |
None |
2% per transaction + GST for domestic cards, UPI, wallets, net banking; 3% + GST for international cards |
None |
Paytm |
None |
2% + GST per transaction; 3% + GST for American Express & Diners Cards |
None |
Stripe |
None |
4.4% + $0.30 per transaction, plus currency conversion charges |
None |
CCAvenue |
Varies according to the plan chosen. |
From 2% to 3% per transaction, depending on the plan. |
Not specified |
Cashfree |
None |
Varies from 1.90% to 2.95% per transaction for different modes of payments |
None |
Are There Any Free Payment Gateways?
PhonePe Payment Gateway eliminates costs for businesses through its free payment system, which includes no setup fees and no transaction or maintenance charges. Free payment gateways help businesses reduce expenses, but they often have limitations, including fewer features and reduced transaction limits as well as less dependable support.
Security & Compliance in Payment Gateways
Payment gateways serve an essential function in safeguarding digital transactions through their protection of sensitive financial data against fraudulent activities and cyber threats.
Major Security Features in Payment Gateways
Leading payment gateways incorporate these essential security features.
1. PCI DSS Compliance
Payment gateways operate under the globally recognized PCI DSS security framework, which establishes secure handling protocols for cardholder data. Compliance with PCI DSS includes.
- Encrypting cardholder information during transmission and storage.
- Regularly update security systems to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Payment gateways can identify and reduce potential threats by performing regular audits.
2. SSL Encryption
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption method converts sensitive information into a format that hackers cannot read, thereby protecting transaction details from unauthorized access or changes. Payment gateways use SSL certificates to provide encrypted connections that protect users’ browsers from phishing attacks and data breaches.
3. 3D Secure Authentication
The 3D Secure protocol introduces an extra verification phase during card payments to protect against unauthorized transactions. During transactions, customers get a one-time password (OTP) or a biometric authentication prompt to confirm their payments. Merchants experience better protection against fraud and fewer chargebacks when they use payment gateways that involve 3DS technology.
Fraud Prevention Measures Used by Top Payment Gateways
Top payment gateways implement sophisticated fraud detection systems to protect transactions. These include the following features.
1. Tokenization
The tokenization process replaces actual card details with a special token that acts as a unique identifier to keep card information hidden. The intercepted token holds no useful value to hackers without the decryption key, which unlocks its meaning.
2. AI-Powered Fraud Detection
Payment gateways that use modern technology analyze transaction patterns through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to identify suspicious activity. This detects:
- Unusual transaction amounts or locations.
- Repeated failed payment attempts.
- Mismatched billing and shipping addresses.
3. Geolocation Tracking & Device Fingerprinting
Payment platforms protect against cross-border transaction fraud by monitoring user location data and device information. Using an Indian-issued card in a foreign country could trigger additional verification steps to safeguard against fraudulent activity.
4. Chargeback Prevention Mechanisms
Chargebacks arise when customers challenge transactions, which results in merchants receiving refunds and experiencing financial losses. This implements:
- Automated risk scoring to decline high-risk transactions.
- Behavioral analysis to detect suspicious account activity.
- Utilize blacklist databases as a security measure to stop fraudulent users from completing transactions.
Read More: Auto Reconciliation
How to Choose the Best Payment Gateway for Your Business
This section lists important considerations for choosing the best payment gateway and compares top options to help you find the best fit for your business.
Factors to Consider
- Cost Structure: Assess the financial impact through a review of setup fees along with transaction charges and ongoing maintenance costs. Analyzing these financial costs enables you to pick a payment gateway that fits your financial plan.
- Security Features: Choose payment gateways that meet industry security standards, such as PCI DSS, while providing strong protection mechanisms like SSL encryption and 3D Secure authentication to safeguard sensitive data.
- Integration Capabilities: Your chosen gateway must integrate flawlessly with your current website or e-commerce platform and provide plugins or APIs for easy implementation.
- Payment Methods Supported: Choose payment gateways that accommodate multiple payment methods, such as credit/debit cards, net banking, UPI, and digital wallets to satisfy different customer preferences.
- Customer Support: Your business operations stay uninterrupted because reliable customer service delivers prompt issue resolutions.
- Settlement Period: Assess the duration required by the gateway to move funds to your account because shorter settlement times can improve your financial liquidity.
Comparison of Leading Payment Gateways
Here is a comparison of some top payment gateways in India.
Feature |
Razorpay |
Paytm |
Stripe |
CCAvenue |
PayU |
Cost Structure |
No setup or maintenance fees; transaction fee: 2% + GST per transaction. |
No setup or maintenance fees; transaction fee: 1.99% + taxes per transaction. |
No setup or maintenance fees; transaction fee: 2%-3% |
Setup fee: Varies according to the plan chosen; annual maintenance fee: ₹1,200; transaction |
No setup or maintenance fees; transaction fee: 2% per transaction. |
Integration |
Offers APIs and plugins for various platforms. |
Provides APIs and SDKs for seamless integration |
Extensive API documentation and SDKs available |
Supports multiple platforms with detailed integration guides. |
Easy integration with major platforms and custom solutions |
Payment Methods |
Supports cards, net banking, UPI, and wallets. |
Accepts cards, net banking, UPI, and Paytm wallet. |
Primarily cards; supports international payments. |
Offers multiple payment options including cards, net banking, and wallets. |
Supports cards, net banking, UPI, and wallets. |
Best Payment Gateway in India: Which One Should You Pick?
Selecting the right payment gateway requires a match between your business requirements and your top priorities.
- For Cost-Conscious Businesses: Paytm offers competitive transaction fees, which cost-conscious businesses can benefit from without having to worry about initial setup expenses or ongoing maintenance costs.
- For Comprehensive Payment Options: CC Avenue provides numerous payment methods alongside multiple currency support, which helps businesses serving diverse customers find it an ideal platform.
- For International Transactions: Stripe’s excellent international transaction support makes it a perfect solution for businesses that serve customers around the globe.
- For Quick Integration and Developer-Friendly Tools, Razorpay’s extensive APIs and plugins enable developers to achieve smooth integration and customization.
Future of Payment Gateways & Emerging Trends
India’s payment gateway sector is experiencing major changes due to technological progress and shifting customer preferences. The current evolution of payment systems is influenced by multiple trends, including the spread of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) systems, artificial intelligence (AI,) and machine learning applications.
Growth of UPI and UPI-Based Payment Gateways
UPI transformed digital payments throughout India by delivering a seamless and instantaneous transaction process. In 2024, UPI processed around 80% of retail transactions in the country which highlights its leading position in the payment system.
The payment gateways PhonePe and Paytm have driven growth by offering intuitive user interfaces alongside comprehensive merchant network connections. The incorporation of UPI into various platforms allows users to complete transactions with ease and has led to widespread digital payment adoption.
Upcoming expansions in UPI-based payment gateways include UPI 2.0, which will offer overdraft options and one-time mandates.
AI and Machine Learning in Fraud Prevention
The increase in digital transactions demands strong fraud prevention systems. Within the field of fraud prevention, AI and machine learning have become essential tools that deliver real-time fraud detection and analysis.
Machine learning algorithms analyze large volumes of transaction data to detect patterns that suggest fraudulent activities. Examining transaction amounts together with frequency and geographical location enables these systems to detect irregularities that prevent unauthorized transactions. AI-driven systems monitor payment flows by identifying duplicate transactions and abnormal payment amounts.
Blockchain and Decentralized Payment Solutions
Payment systems benefit from blockchain technology, which improves their security while speeding up processing times and increasing operational efficiency. The decentralized framework of this system makes transactions clear and permanent, which minimizes fraud risks while building user trust.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) launched the e-rupee as a central bank digital currency (CBDC) to help advance blockchain payment technologies in India. The RBI collaborates with fintech companies, including Cred on the e-rupee digital currency project to refine transaction procedures and elevate user adoption rates.
Read More: Virtual Accounts
Upcoming Regulations in Payment Gateways in India
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) recently decided to prolong the deadline for digital payment companies to meet market share restrictions. The intention behind this move is to establish a fair and competitive marketplace that stops monopolistic behavior and stimulates innovative solutions from payment service providers.
The RBI demonstrates a proactive stance toward technological progress through its digital currency programs, which also include regulatory supervision. The newly introduced measures work to establish a robust payment system that protects and serves the needs of consumers, companies, and financial organizations.
Conclusion
Technological progress together with new regulations and shifting consumer tastes, are transforming India’s digital payment environment at a fast pace. Payment gateways establish secure transaction systems that help businesses, ranging from small merchants to large enterprises, operate smoothly. UPI’s leadership role enables PhonePe, Paytm, and Razorpay to transform transaction methods through improved speed, enhanced security measures, and user convenience.
When choosing their payment gateway, businesses must assess transaction fees along with simple integration security protocols and customer support. A comparison of payment gateways including EnKash, Razorpay, Stripe, PayU, and CCAvenue, allows businesses to determine which platform best fits their specific needs.
The correct payment infrastructure has become an essential component for sustained success across e-commerce, retail, and service-based businesses. Businesses that keep up with new trends and regulatory changes can use digital payments as a growth engine in today’s digital-first environment.