The payment page is a specific web or app page for customers to safely input payment data for completing transactions. As the last stop in the buying process, the payment page holds an essential place in converting potential buyers into paying customers. A well-constructed payment page design ensures the security of sensitive data and user experience, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates and increased trust from customers.
How Does a Payment Page Work?
The payment page is the pivotal point of any online transaction, providing customers with a secure and reliable means to conclude their purchases; this is how a payment page works, step-by-step.
1. Customer Initiation
The payment process starts when a consumer chooses an item or items, places it or them into a shopping cart, and proceeds to checkout. The next step here is for the payment page UI to launch, thereby allowing the customer to review the order details and select on the payment page so that the customer does not abandon their purchase due to confusion or an unnecessary delay.
2. Data Entry
Once a customer lands on the payment page, the next process for them is inputting their payment information. If collected, that information must include such highlights as:
- Credit or Debit Card Information: Card Number, Expiration date, CVV code.
- Billing Address: Verification and fraud prevention.
- Alternative Payment Methods: Digital wallets (e.g., Google Pay, Apple Pay, PayPal) or bank transfers.
- Autofill options for returning customers and saved payment methods improve user experience by speeding up transactions and adding convenience.
3. Data Encryption
The importance of security in online payments cannot be overstated. For their safety, the payment page uses encryption technologies, including SSL (Secure Socket Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security), to guard against any disclosure of sensitive financial particulars. These protocols guarantee that the payment data is effectively transmitted from the customer’s device to the server so that hackers are unable to intercept any of the personal information.
4. Payment Gateway Transmission
After encryption, the payment details entered by the customer are transmitted to a payment gateway, which acts as a connecting channel between the merchant’s website and financial institutions. Payment gateways are responsible for:
- Verification of the details processed for the transaction;
- Confirming that the card or method of payment is valid;
- Encrypting and forwarding the payment data to the acquiring bank or payment processor.
- Payment gateways detect any fraudulent transaction by evaluating multiple parameters like IP addresses, device details, transaction history, etc.
5. Authorization
The customer’s bank or payment processor will receive the transaction request via the payment gateway for its authorization. The bank at this moment checks:
- Sufficient funds or credit limit availability;
- Validity of the card and payment credentials;
- Fraud detection measures (e.g., OTP verification, 3D Secure authentication).
- In the event of all the checks above being cleared, the transaction proceeds.
6. Approval or Decline
The payment requests shall be either approved or rejected depending on the verification by the bank:
Approved: The amount is debited from the customer’s account and transferred to the merchant.
Declined: If the bank detects an issue- funds are insufficient, incorrect details, or expired card- the transaction request is denied, and the customer will receive a notification with an error message. A clear error message describing the reason for declined payment would give customers guidance on what corrective measures should be taken to retry.
7. Completion
The confirmation is sent from the payment gateway to the merchant’s website once the payment is confirmed. The customer is redirected to a confirmation page containing:
- A success message.
- An order summary.
- A receipt (in most cases via email or SMS).
The transaction is, at this time, concluded, and the merchant will go on to fulfill the order for either delivery or service.
Importance of Payment Page Design
A structured payment page does not only influence the transaction experience but also the security features and customer experience as well as the conversion rates. Here are the main reasons businesses should consider designing effective payment pages:
1. Increased Conversion Rates
The more user-friendly and intuitive a payment page is, the lower the checkout friction during the transaction process will be. Payment page properties that will improve conversion rates include:
- Simple, uncluttered design.
- Fast loading.
- Easy navigation and clear payment options.
A slow, cluttered, and confusing payment page will almost guarantee that the would-be customers will abandon their purchase-further translating into lost sales.
2. Trust and Credibility
For online shoppers, security constitutes a huge concern. Consumers want to be assured that their sensitive payment information is going to be secure. By adopting the following, you can earn customers’ trust:
- SSL certificates (represented in the URL as HTTPS).
- Secure Payment icons (Visa Secure, Mastercard SecureCode).
- Transparent refund policy and clear privacy policy.
Emphasizing these will help ease customer apprehensions and propel them to transact confidently.
3. Mobile Compatibility
With a large volume of traffic ordering online via mobile, payment pages have to be responsive and mobile-friendly. A mobile payment page that is well-optimized assures:
- Easier navigation on smaller screens.
- Fast loading.
- Secure autofill for quick checkout.
Otherwise, lost customers and higher cart abandonment rates will be the price of not going mobile.
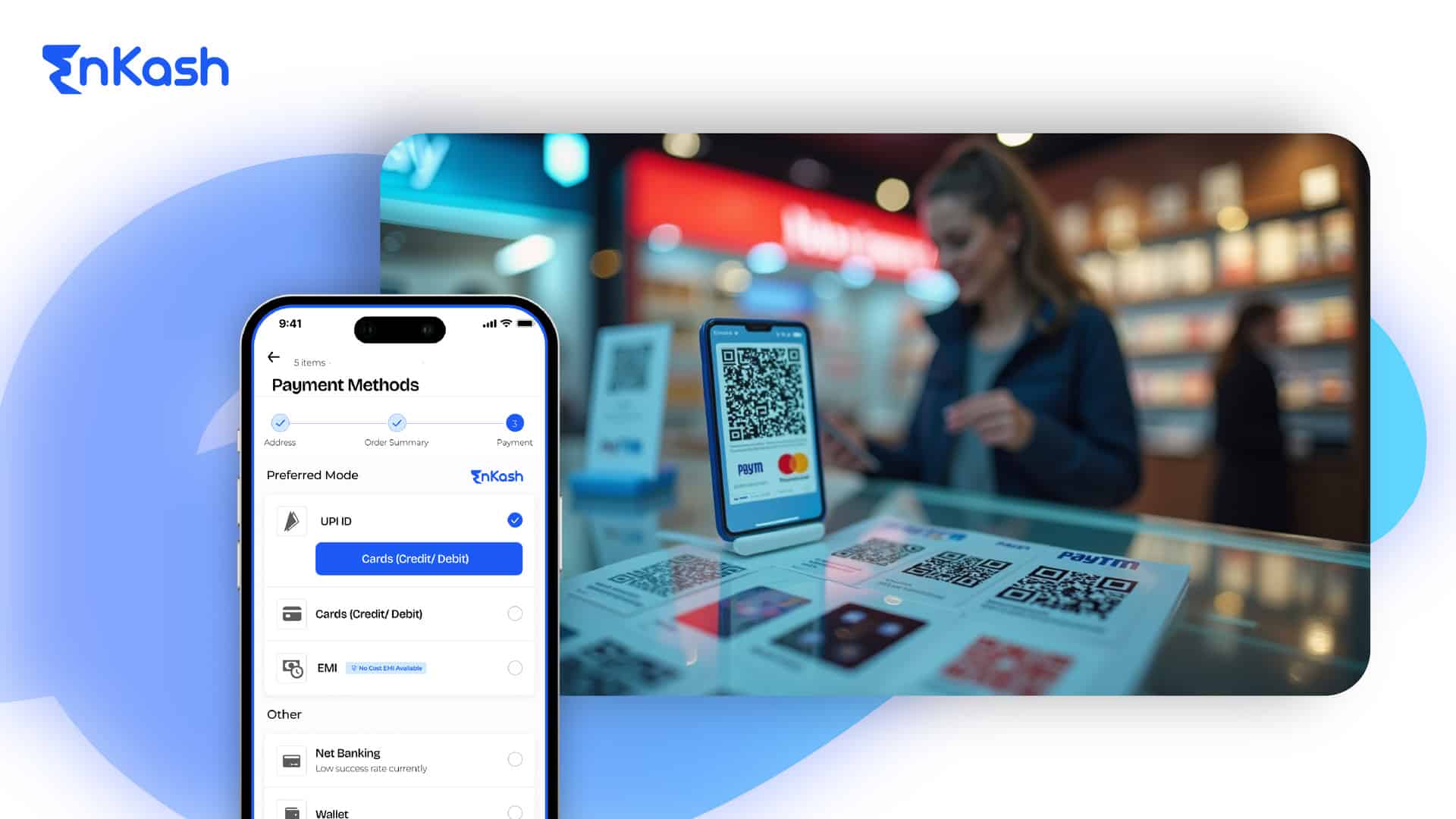
Top Features of Payment Page UI
The payment page UI plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and hassle-free transaction experience. Here are the essential elements:
1. A Clean and Simple Layout
A design that is straightforward and free of clutter allows customers to make payments quickly without any distractions. Things to cover include:
- Minimal form fields.
- Clear headings and instructions.
- Easy-to-read fonts and contrast for better visibility.
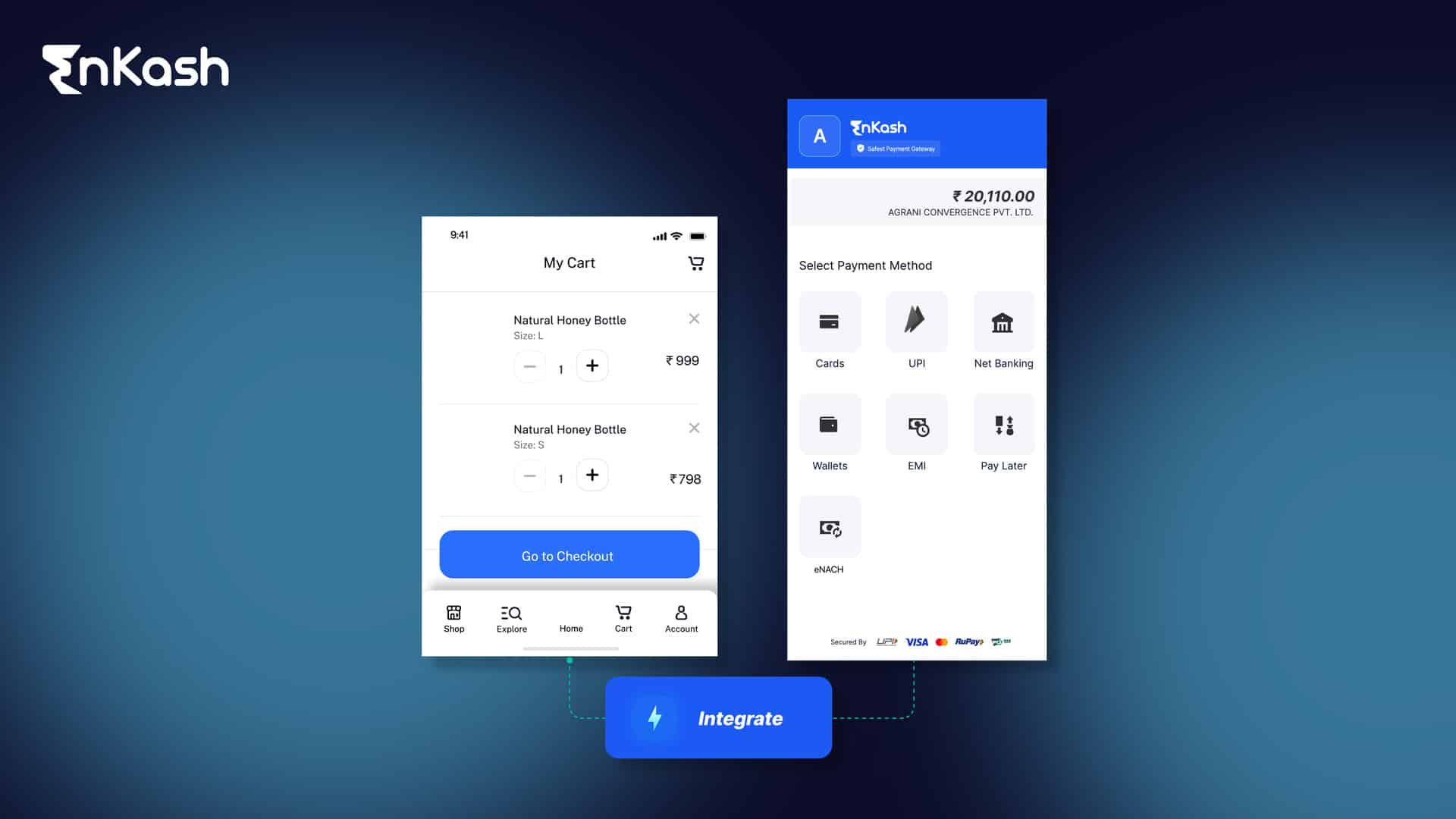
2. Secure Payment Options
Very Important Way to Offer Many Payment Methods-from Credit Cards through Digital Wallets, UPI, and Net Banking Buys Now or Later Easy Way to Reflect Customers Flexibility and Convenience.
Examples of Pay Options are:
- Credit/Debit Cards (Visa, Mastercard, Amex).
- Digital Wallets (Google Pay, Apple Pay, PayPal).
- UPI, Net Banking, and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services.
Providing a plethora of payment options, high accessibility, and high-end customer satisfaction.
3. Progress Indicators
It lets them know where they are in the payment process. In other words, it allows users to keep their expectations clear and set in.
4. Error Messages
The setup is such that:
- The problem is pointed out in clear terms (e.g., “Invalid CVV code”).
- They are delivered in real time so that correction is immediate; clear language instead of generic “Payment failed” messages is very clear.
- This presentation prevents user frustration and reduces drop-offs.
5. Trust Signals
Display of security-related elements reassures customers regarding the safety of their transactions:
- Padlock icons near payment fields.
- SSL certification symbols.
- Logos of trusted payment providers (Visa, Mastercard, PayPal, Stripe).
All these small UI enhancements improve credibility and motivate a buyer toward completing transactions.
Payment Page Template: What to Include?
To plan a payment page template, much thought needs to go into simplicity, security, and user experience. Here are the key components that need to be present in a payment page template:
1. Core Fields
Today, businesses are streamlining payment processes to minimize the number of information fields requiring entry. Fewer fields drive a dramatic improvement in user experience and conversion rates. A payment page should have the following:
- Name on Card: Ensures that the cardholder is correctly identified.
- Card Details: Customers should enter their card number, expiration date, and CVV (Card Verification Value) for authentication.
- Billing Address: Some merchants require this to verify transactions and prevent fraud.
- Email Address & Phone Number: Used for sending receipts and transaction confirmations.
- Alternative Payment Options: Customers should be able to select their preferred payment method, such as credit/debit cards, digital wallets (Google Pay, Apple Pay, PayPal), or direct bank transfers.
2. Pre-filled Information for Returning Buyers
The returning buyer does not need to keep entering their particulars. Pre-filled information speeds up the entire checkout process, which will reduce friction. Some of the strategies that can be adopted include the following:
- Saved Payment Methods: Customers may save their card details for secure future payments.
- Autofill Options: Autofill suggestions can be obtained from saved addresses and payment credentials by the browser.
- Account-Based Checkout: For customers who log in, billing and payment details will automatically be populated.
3. Customization of Brand
There will be an increase in consumer trust and better user experience from a branded payment page. A generic-looking payment page gives customers the suspect factor and, as such, leads to cart abandonment. Key branding elements include:
- Company Logo: It assures them that it is paid to the right entity because they see the business logo.
- Color scheme and fonts: It ensures visual consistency with the website’s design.
- Custom Messages: To engage customers, businesses can add some thank-you messages or promotional banners.
- Customized Payment Confirmation: A well-structured confirmation page gives assurance to customers that they are successful in making the payment.
Best Practices for Payment Page Optimization
Optimizing the payment page is one of the most vital things in reducing cart abandonment and enhancing user experience. Below are some of the best practices:
1. Minimal Form Fields
Most of the checkout forms are lengthy and complex, thus intimidating the customers. The following are some points to reduce this friction:
- Unnecessary fields have been removed, and only essential payment details have been maintained.
- Inline validations would be done under the form, thus giving real-time feedback for any wrong entries.
- Autofill options to speed up input.
2. Various Payment Modes
Given that different customers have different preferences when it comes to payment methods, companies should increase their conversion rates by:
- Including credit and debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, Amex).
- Adding to it, on-the-go and online wallets include: Google Pay, Apple Pay, PayPal, and Amazon Pay.
- Bank Transfers and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL).
- Even now with UPI and Cryptocurrencies (where applicable) methods.
3. Optimize for Speed
A slow payment page causes boredom among users and leads to abandonment. The optimization for speed helps to achieve:
- Compressed images with minimal scripts leave a faster page load.
- Lightweight responsive design that works on all devices.
- Frequently used elements retain caching techniques.
4. A/B Testing
Testing different payment pages with real users will help find out which has the best-converting design. Some of the factors under testing are:
- Placement and color of the button (such as “Pay Now” or “Complete Payment”) –
- Different trust badges and security icons.
- One-page checkout vs. multiple-step checkout.
- Different layouts and builds of forms.
The above are a few examples of the routine testing so that the payment page can be improved in the long run to project maximum efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Payment Page Design
1. Complicated Checkout Processes
A long and indecipherable checkout frustrates customers in processing payments. Some prevention measures include:
- Minimalist design and easy navigation
- Avoid unnecessary steps delaying payments
- A clear CTA like “Complete Payment” or “Pay Securely”
2. Lack of Clear Error Messages
The system fails clearly and promptly to inform customers that they have made a mistake (e.g., expired card, wrong CVV). Mistakes:
- Generic “Payment Failed” messages without explanation.
- Hidden error messages that force users to guess what went wrong.
- No guidance on correcting errors, which leads to frustration.
- Instead, use real-time validation and highlight incorrect fields in red with helpful suggestions.
3. Unsecured Payment Processing
Security breaches may lead to data theft, which in turn will result in the loss of customer trust. Ways of ensuring security include:
- Use of SSL (HTTPS) for securing payment data.
- PCI DSS Compliance (payment card industry data security standard).
- Two-factor authentication (OTP, biometric verification).
- Showing security badges and trust signals (Norton Secured, Verified by Visa) within the page, assuring customers that their payment details are safe.
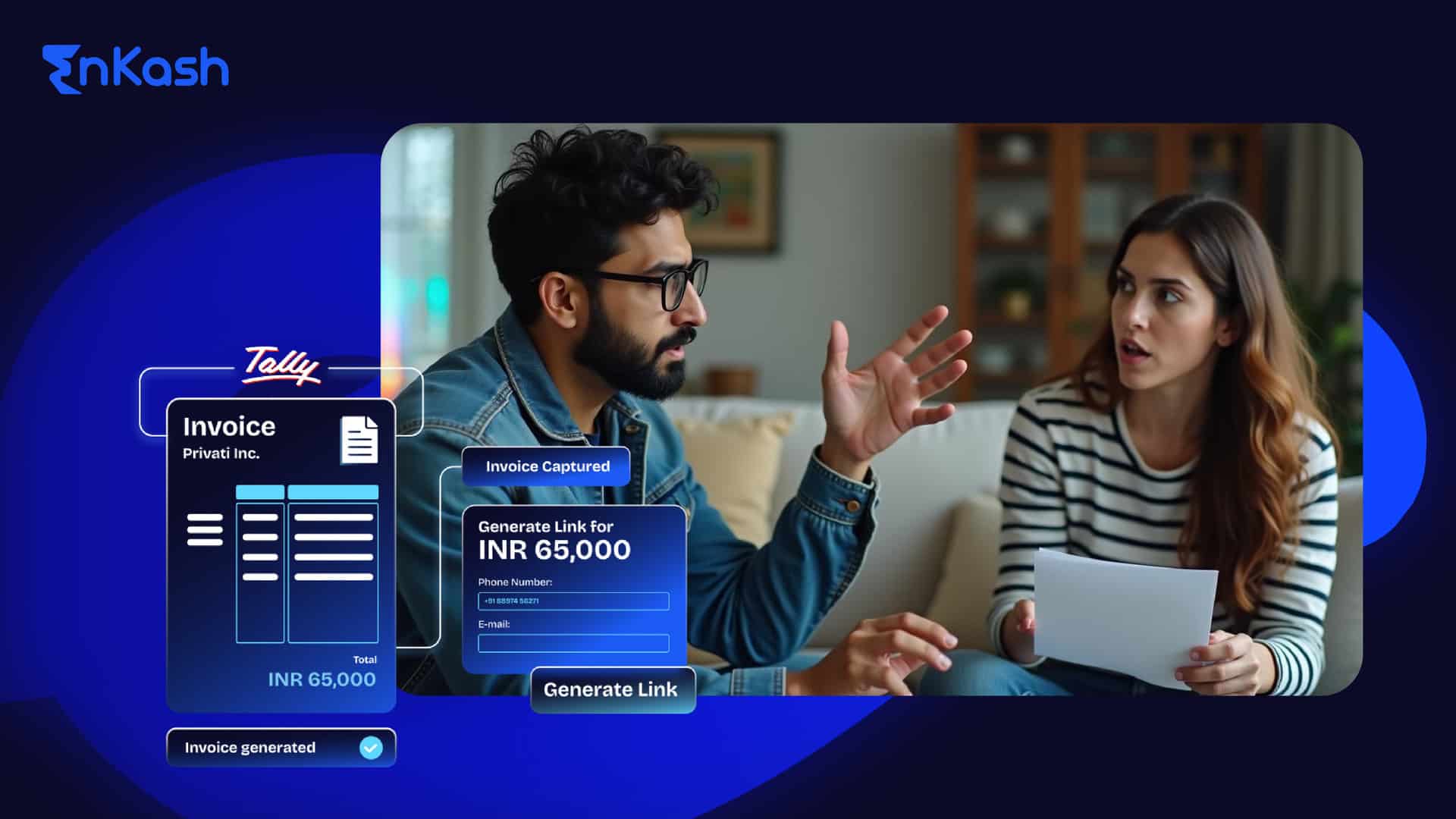
EnKash on Personalized Payment Pages
EnKash provides a seamless way to create customized payment pages tailored to different business needs. Learn more about their approach here.
1. Minimal Integration for Hassle-Free Setup
EnKash offers a quick and easy setup of the pay page, needing so little technical know-how at all. Businesses can, therefore:
- Integrate payment gateways easily with a few lines of code.
- Collect securely for one-time and recurring online payments.
- Modify the entire flow of payments according to business needs.
2. Multiple Payment Pages for Different Transactions
Unlike old checkout pages, EnKash allows:
- Businesses create different payment pages according to the transaction type.
- Create separate donation pages for an individual’s contribution, customer invoices, and subscription payments.
- A real-time view of payment transactions would help businesses in better financial management.
3. Advanced Security Features
EnKash has strict security protocols:
- Customer privacy is ensured through the non-storage of card details.
- Data is encrypted and securely transferred between customers, payment gateways, and banks.
- Industry security standards are adhered to prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
4. Automated Receipts for Payments
Generating a receipt manually takes a huge amount of time. EnKash automates the entire process:
- Receipt generation occurs instantly after the payment confirmation.
- Transaction details are sent to the customers via email and SMS.
- Receipt templates are customizable to an organization’s branding.
Conclusion
A well-optimized payment page ensures a smooth and secure transaction experience, impacting customer satisfaction and business revenue. A payment gateway’s intuitive design, strong security measures, and ongoing optimization together enhance the payment experience for businesses. EnKash demonstrates these ideals by providing customizable, secure, and efficient payment solutions to satisfy different business needs.