Corporate card for businesses are an essential tool for streamlining expenses and facilitating employee purchases. However, with this convenience comes a responsibility to ensure the security of these cards and prevent fraudulent activity. Corporate card fraud can be a significant financial burden for businesses, leading to lost revenue and reputational damage.
In this article we will learn about the importance of security and controls for corporate cards, outlining the different types of fraud and the measures you can take to safeguard your company’s financial well-being.
Understanding the Threat: Corporate Card Fraud Types
Corporate card fraud can take various forms, each requiring a different approach to prevention. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
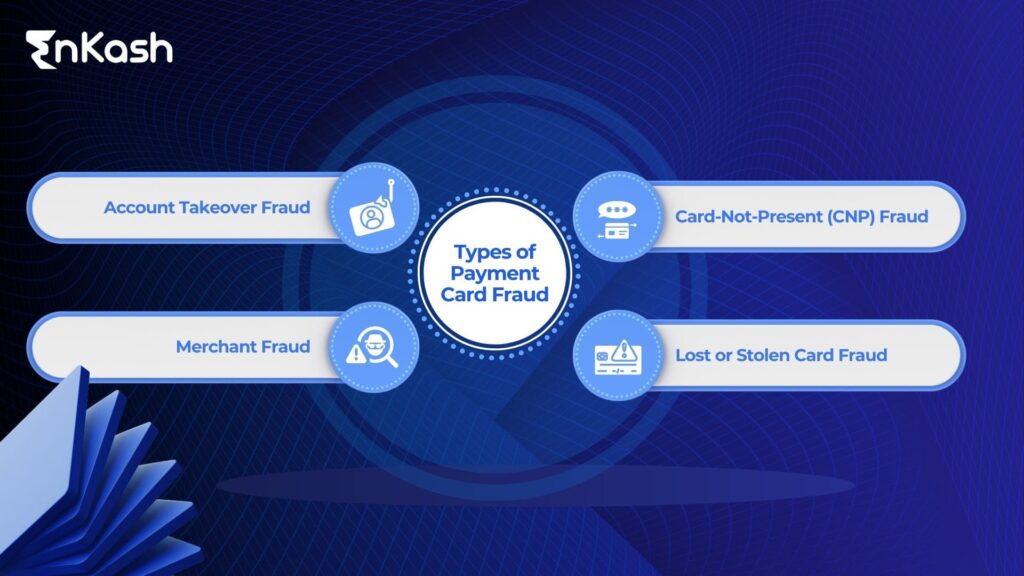 Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud:
Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud:
This is the most prevalent corporate card fraud type, accounting for roughly 75% of all card fraud. It happens when your card details are used to make a purchase without the physical card being present. Here are some common ways CNP fraud occurs:
Phishing scams: Fraudsters send emails or text messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as your bank or a familiar retailer. These messages often try to trick you into clicking on a malicious link or providing your card information on a fake website.
Malware: Malicious software (malware) can be installed on your computer or phone without your knowledge. Some malware can steal your card information when you enter it on a website.
Data breaches: When a company’s database is hacked, fraudsters may be able to steal customer information, including credit card numbers. They can then use this information to make unauthorized purchases.
Lost or Stolen Card Fraud:
This type of fraud is more straightforward. If your physical credit card is lost or stolen, thieves can use it to make unauthorized purchases. This is why it’s important to report a lost or stolen card to your bank immediately.
Account Takeover Fraud:
This fraud occurs when someone gains unauthorized access to your online credit card account. They can then use your account information to make unauthorized purchases or transfers. Here are some ways fraudsters might take over your account:
Account cracking: Fraudsters use various techniques to guess or hack your login credentials. This can be done through automated attacks or by using information obtained from data breaches.
Social engineering: Scammers might use social engineering tactics to trick you into revealing your login information. For instance, they might call you pretending to be from your bank and ask for your credit card details to resolve a fictitious issue.
Merchant Fraud:
In this less common scenario, a seemingly legitimate merchant processes fraudulent transactions on your card. This could be due to a number of reasons, such as:
Card skimming: Fraudulent merchants may use skimming devices to steal card information from customers who swipe their cards at their terminals.
Data breach: If a merchant’s system is hacked, customer card information may be stolen and used for fraudulent transactions.
Processing errors: In rare cases, processing errors by the merchant might lead to duplicate charges or other billing mistakes.
Corporate Card Security Tips
Here’s a detailed breakdown of security controls you can implement to create a multi-layered defence against corporate card fraud:
Preventative Measures:
These corporate care rules aim to proactively prevent fraudulent activity from happening in the first place.
Issuance and Access Control:
Limit card issuance: Only issue cards to employees who genuinely require them for business purposes. Don’t assign cards unnecessarily
Right Fit, Right Card: Assign cards with spending limits and functionalities (physical vs. virtual) tailored to each employee’s specific role and spending needs. A marketing manager wouldn’t require the same card as a field technician
Spending Limits:
Establish spending limits for each card based on an employee’s average spending patterns and job responsibilities. This deters unauthorized high-value purchases
Consider tiered limits for recurring expenses versus one-time purchases
Merchant Category Code (MCC) Controls:
Implement MCC controls to restrict purchases to specific merchant categories relevant to the employee’s job function. This prevents misuse for personal expenses (e.g., restricting office supply purchases to authorized office supply stores)
Geo-fencing:
Utilize geo-fencing technology to restrict card usage to specific geographic locations that align with the employee’s typical business travel needs. This helps prevent unauthorized international transactions unless absolutely necessary
Card Verification Value (CVV) Controls:
Mandate the use of CVV codes for all online and phone transactions. Since CVV codes are not typically printed on receipts, requiring them adds an extra layer of security against unauthorized transactions where fraudsters might have obtained the card number
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Implement MFA for online access to corporate card accounts. This requires an additional verification step beyond just a username and password, such as a code sent to the employee’s mobile phone. This significantly increases the difficulty for unauthorized individuals to gain access to the account
Regular Reviews and Monitoring:
Conduct periodic reviews of card activity, looking for anomalies or suspicious spending patterns. Analyze reports for unusual purchase times, locations, or vendors
Consider fraud detection software that leverages AI and machine learning to identify potentially fraudulent transactions in real-time
Reactive Strategies:
While prevention is key, these corporate card rules help mitigate damage in the event of a security breach:
Fraud Alert Systems:
Utilize fraud alert systems that notify you of unusual card activity in real-time. Set up alerts for transactions exceeding spending limits, purchases from unauthorized locations, or a sudden increase in transaction frequency. Prompt action can minimize losses.
Card Deactivation:
Have a system in place to quickly deactivate lost or stolen cards. This can often be done through a mobile app or online portal associated with the card issuer. The faster a compromised card is deactivated, the less potential for fraudulent activity.
Reporting Procedures:
Establish clear procedures for employees to report lost or stolen cards or suspected fraudulent activity. This might involve a dedicated hotline, online reporting system, or contact information for a designated fraud response team. Easy reporting encourages employees to act swiftly when they suspect a problem.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Security Measures
Enforce Policies:
A well-defined corporate card policy acts as a clear roadmap for employees, outlining acceptable card usage, spending limits, and employee responsibilities regarding card security. Key elements of the policy should include:
Eligibility: Clearly define who is eligible to receive a corporate card based on job function and spending needs
Acceptable Use: Explicitly state what constitutes authorized business purchases with the card and what personal use is strictly prohibited. Provide clear examples to avoid ambiguity
Spending Limits: Establish spending limits for each cardholder based on their role and typical expenses. Consider tiered limits for recurring expenses versus one-time purchases
Recordkeeping Requirements: Outline the specific documentation required for each transaction (e.g., receipts, invoices) and how long employees must retain them
Security Protocols: Detail security measures employees must follow, such as using strong passwords, safeguarding card details, and reporting lost or stolen cards immediately
Consequences for Misuse: Outline the disciplinary actions that will be taken in case of policy violations or suspected fraudulent activity
Educate Employees
Regular employee training on the corporate card policy is crucial. Educated employees become active participants in safeguarding company resources. Training should cover:
Policy Overview: Thoroughly explain the key aspects of the corporate card policy, ensuring everyone understands their rights and responsibilities
Fraud Awareness: Educate employees on different types of card fraud and how to identify suspicious activity (e.g., phishing scams, unusual charges)
Reporting Procedures: Clearly outline the process for employees to report lost or stolen cards, suspicious charges, or potential fraud attempts
Security Best Practices: Train employees on secure card handling practices, such as using strong passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi for financial transactions, and never sharing card details with unauthorized individuals
How can EnKash help?
At EnKash, we understand the importance of corporate cards security features and offer a comprehensive suite of corporate card solutions with robust security features. Our platform incorporates many of the controls mentioned above, including spending limits, merchant category code restrictions, and real-time transaction monitoring. Additionally, EnKash offers features like virtual cards for added security in online transactions and instant expense reports for greater transparency and control.
We adhere to the strictest industry standards, ensuring the highest level of data protection. We are fully PCI DSS compliant, signifying that our systems meet rigorous security requirements and all data transmitted and stored on our platform utilizes robust encryption protocols, safeguarding sensitive financial information.
In Conclusion
Corporate card for businesses are a valuable tool for businesses, but with that value comes the responsibility for security. By implementing the security controls and best practices outlined in this article, you can create a safe and secure environment for corporate card usage. Remember, a proactive approach to security combined with employee education is key to keeping your corporate cards safe and your business finances protected.