When the shares of a company are offered in the capital markets (stock exchanges) for trade, it is known as an Initial Public Offering or IPO. The shares are commonly offered to institutional and retail investors (i.e., individuals).
For an IPO to take place, a private company is transformed into a public company. Every private company wants to achieve this milestone because it helps them raise capital for various business ventures and provides exit paths to investors. Post the company is listed, its shares are listed on the stock exchange for trading in the stock market. Read on to learn more about IPO in detail.
IPO: Key Points
- A company and its existing shareholders offer fresh and existing shares to the public in exchange for capital, and the company then uses this capital for growth
- Once the company is public, it gives them a good shot at building a brand since IPOs are covered by the media, extensively
- The approval for Initial Public Offering, i.e., listing on stock exchanges, is granted by a regulatory authority and in India, it is the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- It is a perfect opportunity for the company to create wealth for the key stakeholders
- Going public has its benefits for the employees who have ESOPs as well they can publicly trade their shares post exercising
- Fixed price for an IPO is determined based on the number of bids at different price points and the valuation of the Company.
What is the Need for IPO?
- The foremost reason companies want to offer their shares via an IPO is easy to access huge capital easily and instantly
- Another important reason companies want to get publicly listed is that it adds credibility to the company in the industry.
- Approval for IPO by SEBI is granted post thoroughly going through various disclosures by the Company on its business, regulatory and litigation risks etc, thus a final approval speaks volumes of company’s credibility.
- It offers an exit route for private investors who wish to sell off their shares at huge profits
- The company gets valuable leverage for negotiating lower interest rates on loans for future needs
Eligibility Criteria for Filing an IPO
- Below mentioned are the most requirements for filing an IPO:
- The company should have at least existed for three years
- Having a PAN no, Demat is of utmost importance for filing an IPO
- The net worth of the company should be positive
- At least 25% of the company must be owned by the public (i.e., not held by promoters or related parties)
How Does the Initial Public Offering Work?
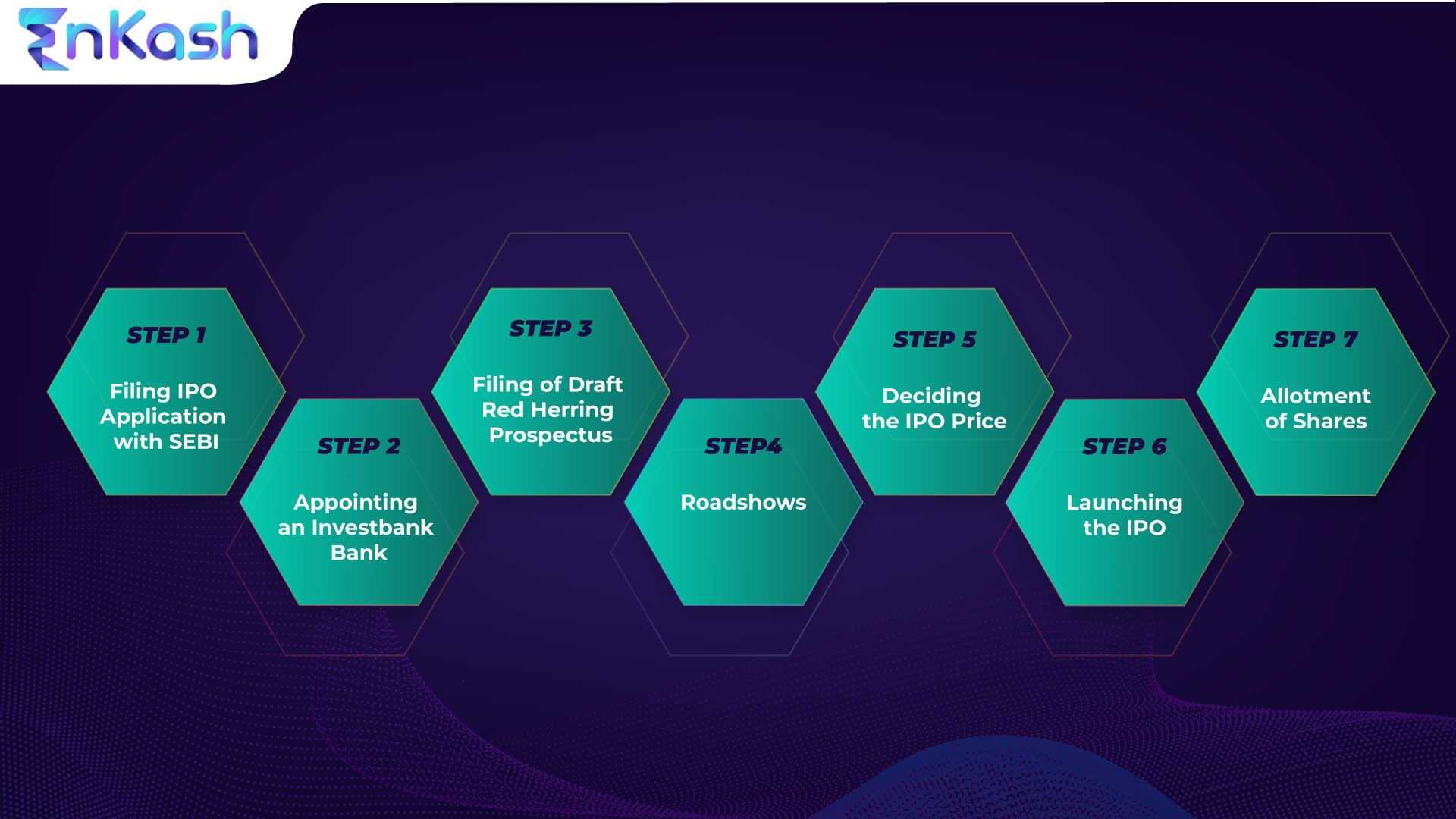
Before an IPO is approved, it undergoes a long process by the regulatory authority to determine eligibility for filing an IPO. The steps involved are as follows:
- Filing IPO Application with SEBI: To start the Initial Public Offering process, applying with SEBI along with all the relevant details is necessary, such as:
- Number of shares to be issued
- The price set (in case it is fixed price IPO)
- Previous records of the company
- Proposed use for the funds to be raised, etc.
- Appointing an Investment Bank: (also called the Left lead): This person is approached on a contract basis and is responsible for managing the sales of the IPO. They guide the company in raising capital and act as intermediaries between the company and its investors. They are also an intermediary between the Company and SEBI. T
- Filing of Draft Red Herring Prospectus: The company issues Draft Red Herring Prospectus (RHP) with SEBI containing details about the IPO, the company’s business, its capital structure, risks, regulations, and litigation as per the materiality threshold.
- Roadshows: Before the IPO is open to the public, companies usually create a buzz in the market by advertising the impending IPO across the country via various presentations to help investors better understand the positive aspects of the particular IPO.
- Deciding the IPO Price: As the next step, the company initiates the IPO price through Fixed Price IPO or Book Binding offering.
- Launching the IPO: The company launches the IPO after finalizing the size and brand. It is the responsibility of the lead manager to contact all potential investors.
- Allotment of Shares: As the last step in the IPO process, shares are allotted to the investors on the basis of the bids made. The allotment process is done through a computerized system, which ensures that the shares are fairly priced.
Note: The IPO is open for subscription by eligible investors only for a specified period. The investment bank arranges the issue’s opening on behalf of the company according to SEBI guidelines.
Also, the process of IPO can be complex and time-consuming, and it may take several months or even years for a company to go public successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the price band mean in IPO?
The Price Band refers to the lower and upper limit of the share price within which the company decides to offer its shares to the public. The investors can bid equal to or between these lower and upper limits.
Can I apply for multiple IPOs from the same name and company?
No, multiple applications are not accepted by SEBI for IPO.
Who are Investment Bank?
Investment Bank is an independent financial institution appointed by the company going public to manage the IPO on its behalf. They are also called Book Running Lead Managers and are registered with SEBI to act as an intermediary between SEBI and the Company.
What is Red Herring Prospectus?
A red herring is a preliminary prospectus filed by a company in connection with the company’s initial public offering (IPO).