The banking sector is constantly evolving and revolutionizing the way individuals and businesses carry out financial transactions. Traditional methods of handling cash are being replaced by digital payment services that offer convenience, speed, and security. One such digital payment service is IMPS, which stands for Immediate Payment Service. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the meaning, full form, benefits, and differences between IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS.
IMPS Full Form and Meaning
IMPS, which stands for Immediate Payment Service, is an online money transfer service offered by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). It allows individuals and corporations to electronically transfer funds from one bank account to another in real time. IMPS transactions are available 24x7x365 days, providing users with the convenience of instant money transfer.
Features of IMPS
IMPS or Immediate Payment Services is the system where money transfer can be made very fast with great reliability and secure digitization. It was introduced to ensure immense convenience for the users, and over the years, IMPS has become widely adopted as a money transfer mechanism in India. Here are the salient features of IMPS:
Instant Transfer
With IMPS, instant transactions guarantee that the money is credited instantly to the account of the money beneficiary. In this case, IMPS is the service for the very urgent transactions, where time plays a vital role.
Availability Throughout the Year
It is available 24×7 all through the year including weekends and bank holidays, so much unlike the conventional banking services that operate on fixed working hours. So with IMPS, users can always transfer funds regardless of time.
Flexible Limits on Transfers
IMPS is designed for both small and medium transfer values. The minimum limits are set at ₹1 while the maximum limit to be transferred within a day is set at ₹5 lakh by policy of each bank.
Different Access Channels
You can access IMPS through different modes like:
– Internet banking
– Mobile banking application
– ATMs
– SMS-based services
This actually makes it flexible in choice for the user to prefer their mode of doing a transaction.
Transaction Security
IMPS has a very high standard of security based on encryption and multi-layer authentication, which guarantees the protection of sensitive user data and also renders transactions free from fraudulent or unauthorized access.
Instant Confirmation
Instant Confirmation of the transaction on SMS or emails to both Sender and Receiver. Transparency is added to the transfer mechanism and also uncertainty regarding the status is diminished.
Simple Transaction Process
IMPS requires very little information to initiate a transfer. Payments can be done through a recipient’s mobile number and MMID (Mobile Money Identifier) or to the account number and IFSC code of the beneficiary. This makes IMPS all the more user-friendly for digital fund transfers.
Available for All
Individual customer and institutional use has made it accessible to one and all. It is useful in various financial purposes, such as bill payments, salary transfers, personal outward remittances, etc.
NEFT Full Form and Meaning
NEFT, which stands for National Electronic Funds Transfer, is a fund transfer mode introduced and operated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It enables individuals and organizations to electronically transfer money from one bank account to another. NEFT operates on a centralized payment system and is available 24x7x365 days. To initiate NEFT transfers, individuals can visit their bank branch.
RTGS Full Form and Meaning
RTGS, which stands for Real-Time Gross Settlement, is another payment system that facilitates funds transfer from one account to another. However, unlike IMPS and NEFT allow processing of transactions in batches. RTGS is designed for high-value transactions only. To be eligible for an RTGS transfer, the transferable amount should be greater than or equal to 2 lakh.
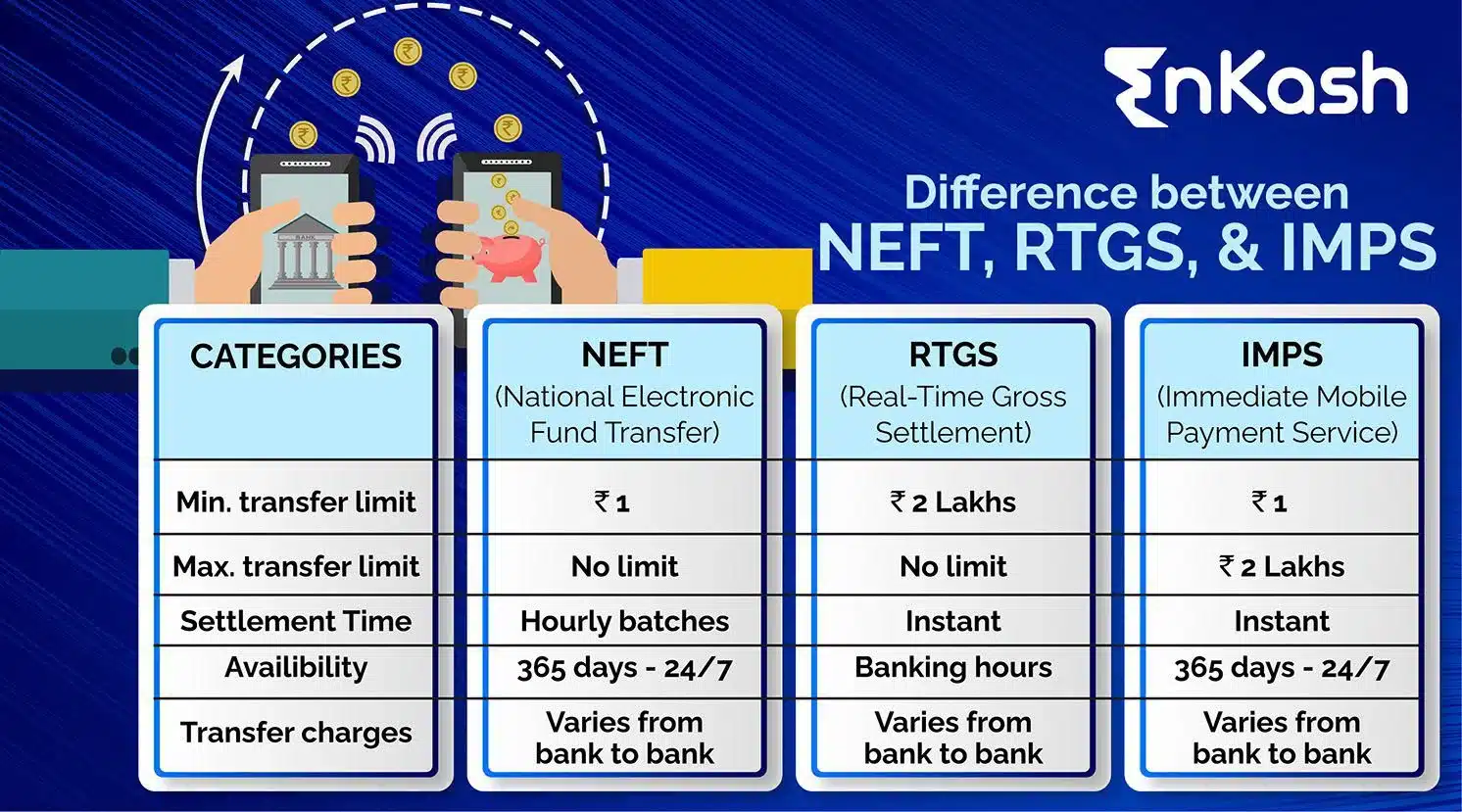
What are the Difference Between IMPS, NEFT and RTGS?
NEFT and RTGS were introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), while IMPS was introduced by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). Collectively, these payment systems have simplified the fund transfer process, eliminating the need for frequent visits to bank branches and reducing transaction charges. However, each payment system has its unique characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at the differences between NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS.
Categories |
IMPS |
NEFT |
RTGS |
|---|---|---|---|
Governing Body |
Built by the National Financial Switch network and managed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). |
Owned and operated by the Reserve Bank of India. |
Owned and operated by the Reserve Bank of India. |
Settlement Process |
Instant money transfer into the beneficiary’s account. |
Works on a net and batch basis. Payments are released in batches, with a minimum gap of 30 minutes. |
Instant money transfer into the beneficiary’s account. |
Service Timings |
Available 24x7x365 days |
Available 24x7x365 days |
Available 24x7x365 days |
Minimum Transfer Limit |
₹ 1 |
₹ 1 |
₹ 2 lakh |
Maximum Transfer Limit |
₹ 5 lakh per day |
No NEFT limit set by RBI. Charges may vary from bank to bank. In the case of cash transactions, the maximum limit is ₹ 50,000. |
No RTGS limit is set by RBI |
Transaction Charges |
Charges vary from one bank to another |
No charges for online transactions. Charges are applicable when the fund transfer is initiated at a bank branch. Charges vary from one bank to another. |
No charges for inward and online transactions. Charges may be applicable for outward transactions. |
Mode of Payment |
Online |
Online |
Online |
How to Transfer Money Through IMPS?
Transferring money through IMPS is quite easy, fast, and can be done using various modes like Mobile Banking, Internet Banking, or ATM. Here is a step-by-step procedure for carrying out the fund transfer:
1. Mobile Banking:
- Login to your bank’s mobile banking application.
- Go to the Fund Transfer Section and choose IMPS.
- Pick up the transfer method:
- MMID-requires the mobile number of the recipient as well as MMID.
- By Bank Account and IFSC code.
- Beneficiary details with the amount entered for transfer.
- Confirm with either mobile banking PIN or OTP.
- You’ll get an instant confirmation with the details of a transaction.
2. Through Internet Banking:
- Log in to the online banking portal provided by your bank.
- Choose the option Fund Transfer, then IMPS.
- Fill in Beneficiary details if new (account number/IFSC code/mobile number with MMID).
- Enter the transfer amount, confirm and send.
- Authenticate using OTP/Transaction password.
- Both the participants will receive an alert upon successful transfer completion.
3. Through ATMs:
- Visit ATMs, insert your debit card.
- There, you will find the option Fund Transfer.
- Choose IMPS for transfer modes.
- Type in the national mobile and bank number alliance code for the person identified with the account you want to send money to.
- Transfer the amount and confirm the transfer.
- Last, collect the receipt, as it contains reference number against the transaction performed.
4. SMS Banking:
If your bank has enabled the SMS-based IMPS fund transfer, send the standard SMS format (as per the bank) containing the beneficiary’s details and transfer amount to the number given by the bank.
Then authenticate the transaction using the PIN or password sent to your mobile.
You will receive an SMS confirming the transaction.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS
When selecting between IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS for fund transfers, there are several factors to consider:
Transaction Charges: Each payment system may have different transaction fees. It is important to compare the charges for IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS and choose the option that offers the best value for money.
Bank Policies: Transaction charges may vary from bank to bank. It is advisable to find a bank that charges the least fee for fund transfers.
GST Charges: Consider the Goods and Services Tax (GST) charges levied per transaction when calculating the total payable fee.
Processing Time: Different payment systems may have varying processing times. It is important to choose a payment mode that meets your time requirements.
Transfer Limits: Each payment mode has a fund transfer limit.
Availability: IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS are available 24x7x365 days, allowing you to initiate fund transfers anytime.
Bulk Payments: NEFT Vs RTGS Vs IMPS
Contrary to common belief, IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS can also be used for making bulk payments. Bulk payments refer to a payment system that enables merchants to pay off numerous vendor payments in one go. This can include remitting employee salaries, reimbursing expenses, and sending pension contributions to a large list of people.
To make bulk payments via NEFT/RTGS/IMPS, merchants can follow these steps:
– Register for CMS – Bulk NEFT/RTGS/IMPS facility with an authorized bank
– Gain access to the web portal
– Upload the payment file or the bulk list
– Verify vendor details along with the amount payable
– Authorize the payment file or the bulk list
– Make the payment and generate Management Information System (MIS) reports
IMPS Vs NEFT Vs RTGS Vs Other Payment Modes
In addition to IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS, there are several other payment modes available in the market. These innovative payment systems have been introduced by the fintech industry, offering more sophisticated ways to make and receive instant payments. Let’s explore some of these payment modes and understand how they differ from the traditional ones.
Unified Payment Interface (UPI): Regulated by the Reserve Bank of India, UPI facilitates inter-bank fund transfers through mobile phones. To use UPI, individuals need to download the UPI app on their smartphones, register with their mobile number, link their bank account(s), and create a UPI PIN. Common UPI apps in India include BHIM, Paytm, Google Pay, and PhonePe.
E-wallets: E-wallets are virtual wallets that enable cashless transactions anytime, anywhere. Similar to credit and debit cards, e-wallets can be loaded with money to make payments whenever needed. As a merchant, you can also accept payments in your e-wallet by registering with one of the platforms, obtaining your own QR code or e-wallet ID, and receiving payments from customers.
Payment Links: Payment links are a relatively new concept in the fintech industry. They allow merchants to send payment links to customers via email, SMS, or other communication channels. Customers can then open the link and make the payment using various options such as credit/debit cards, UPI, e-wallets, net banking, and more. Platforms like Enkash, enable merchants to generate payment links in bulk, saving time and reducing errors. Payment links are a quick, easy, and convenient way for both customers and merchants to make and receive payments.
Debit Cards: Debit cards are bank-issued payment cards that deduct money directly from the cardholder’s bank account when making a purchase. They provide an excellent alternative to cash and offer the convenience of making instant payments using a chip and PIN. Debit cards can also be used contactless or through mobile devices.
Credit Cards: Credit cards are similar to debit cards, but with one key difference. Instead of deducting money from the bank account immediately, credit cards allow the cardholder to pay the amount at a later date, usually within 30 days. Credit cards come with a set credit limit that can be used for payments or purchases. They can be used for online payments, chip and PIN transactions, contactless payments, and mobile payments.
Prepaid Cards: Prepaid cards are an alternative to cash, debit cards, and credit cards. Unlike debit and credit cards, prepaid cards do not require a bank account. Users can load money onto the card and use it until the balance runs out. Prepaid cards can be used for online payments, in-store purchases, and at any other location that accepts them.
IMPS Charges and Transaction Limits
IMPS charges and transaction limits vary depending on the bank. Here’s an overview:
1. IMPS Charges
IMPS transactions may have nominal fees depending on the amount of transfer and the policies of banks. Fees for IMPS are usually within these ranges:
Free IMPS transactions, performed through mobile or internet banking, may be limited in number during a month.
IMPS transaction charges would usually fall within these bands:
From ₹1 to ₹1,000: Charges Nil or Very Low (₹2 to ₹5).
From ₹1,001 to ₹1 lakh: Charges per transaction would range from ₹5 to ₹15.
From ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh: Charges per transaction would range from ₹15 to ₹25.
Charges may also include applicable Goods and Services Tax (GST).
2. IMPS Transaction Limits
Minimum Transfer Limit: ₹1.
Maximum Transfer Limit:
For almost every bank, the IMPS limit is set at ₹5 lakh for a day.
Some banks may have low daily limitation depending on the account type though.
Users can look at their banks for specific IMPS transaction limits through internet banking or call customer service.
3. Bank Policy on Charges and Limits
It varies with banks, so for every person, it is advisable to check the terms with his/her bank before undertaking some larger transfers.
IMPS Charges for Most Banks Will be Waived for Premium Account Holders or Regular Users of Mobile Banking.
Know all these IMPS features along with the stepwise procedure for using this service and charges applicable to it, so that it can be put to good or even great use for seamless fund transfers by individuals and businesses.
The Role of Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in the Banking Sector
While IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS are the core banking services that have improved fund transfer processes, they may not be sufficient or user-friendly for merchants. This is where Payment Service Providers (PSPs) come into play. PSPs are complete payments and banking platforms that help merchants handle their payment and banking needs efficiently.
The role of PSPs includes:
Handling Regulations: PSPs ensure compliance with various regulations, such as PCI-DSS compliance, and other legal formalities to ensure smooth transactions for merchants.
Security: PSPs implement encryption and security measures to minimize the risk of fraudulent activities and protect sensitive information.
Recurring Payments and Bulk Transfers: PSPs handle recurring billing, payouts, and bulk transfers, simplifying these processes for merchants.
Multiple Payment Methods and Currencies: PSPs offer a wide range of payment methods and currencies, allowing merchants to expand their customer base and accept international payments.
Account Management and Insights: PSPs provide intuitive dashboards for managing accounts and gathering business insights to make informed decisions.
PSPs like EnKash offer a comprehensive solution for merchants, providing a seamless payment experience and enabling them to focus on their core business activities.
The Future of Online Payments in India
The Indian payments industry has witnessed significant growth and transformation in recent years. The introduction of new payment systems and advancements in financial technology have revolutionized the way people transact digitally. Initiatives like UPI, payment links, QR codes, e-wallets, and prepaid cards have made payments more convenient and accessible for individuals and businesses.
The ongoing digital revolution is reshaping traditional banking services and driving merchants and individuals to embrace innovative solutions. Fintech companies and payment service providers continue to explore technologically advanced means to enhance existing payment systems and introduce new ones. These advancements aim to streamline the payments ecosystem, provide personalized customer experiences, and create new revenue streams.
Currently, payment solutions focus on real-time, low-value, high-volume, peer-to-peer payments, as well as eCommerce payment options. As the Indian fintech sector continues to innovate, we can expect more advancements that will shape the future of online payments, making them even more efficient and sought-after.
Conclusion
The evolution of the banking sector, marked by the transition from traditional cash handling to digital payment services like IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS, has significantly transformed the way individuals and businesses conduct financial transactions. Each of these payment systems offers unique features, benefits, and transaction limits, catering to diverse user needs. Factors such as transaction charges, processing time, transfer limits, and availability should be considered when choosing between them. Additionally, the guide explores other innovative payment modes like UPI, e-wallets, payment links, debit cards, credit cards, and prepaid cards, emphasizing the continuous advancements in the fintech industry. Payment Service Providers (PSPs) play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and user-friendliness of these payment systems for merchants. Looking ahead, the future of online payments in India is expected to witness further technological advancements, driving the industry towards increased efficiency, personalized customer experiences, and the introduction of new revenue streams. The ongoing digital revolution continues to reshape traditional banking services, making online payments more accessible and convenient for a wide range of users.
FAQS on IMPS vs NEFT VS RTGS
Q1. Which is better, IMPS or NEFT?
A: The choice between IMPS and NEFT depends on the fund transfer requirements. For larger transfers, NEFT is a better option, while IMPS is more suitable for smaller instant transfers.
Q2. Is IMPS transfer free?
A: IMPS charges vary depending on the amount being transferred and the bank’s policies. Some banks offer free IMPS transfers, while others may charge a nominal fee.
Q3. Is Google Pay NEFT or IMPS?
A: Google Pay is neither NEFT nor IMPS. It is a UPI-based payment platform that enables inter-bank fund transfers through mobile phones.
Q4. What’s the best way to send money: UPI, IMPS, or NEFT?
A: The best way to send money depends on the specific requirements. NEFT is suitable for larger transfers, UPI is convenient for day-to-day transactions, and IMPS is ideal for instant smaller transfers.
Q5: How many times can NEFT transactions be done in a day?
A: You can carry out as many NEFT transactions as you want until you reach the NEFT transfer limit set by your bank.