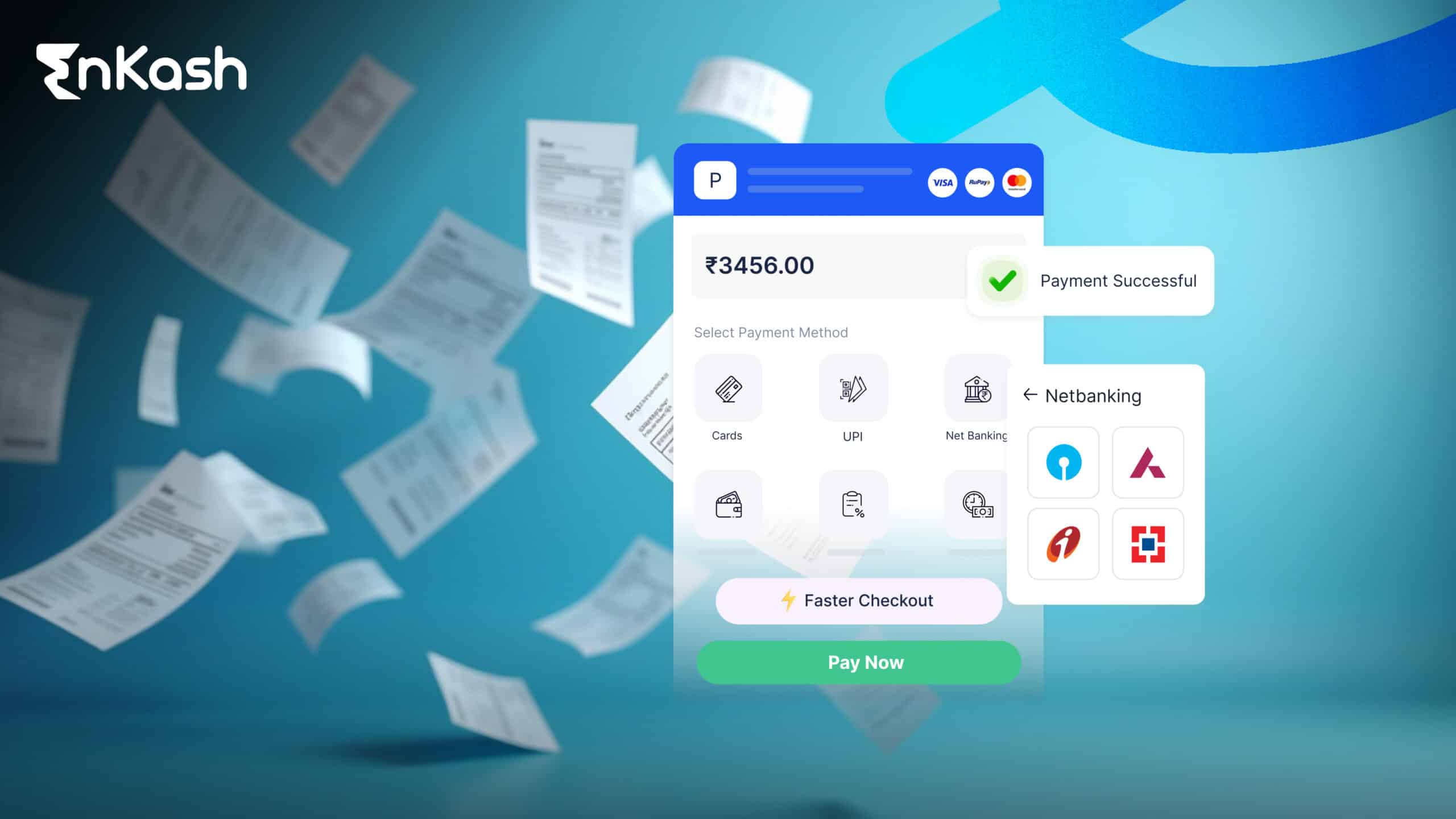
More than ever, in this digital age, businesses rely increasingly on online payment processing methods to consummate fast and secure transactions with customers. A secure payment gateway enables businesses to manage their digital payments with credit cards, debit cards, UPI, and digital wallets. It acts as a bridge or link between the issuing bank of a customer and the acquiring bank of the merchant by ensuring smooth and secure transactions of payments. For any e-commerce shop, online subscription service, or marketplace, effective integration of the right payment gateway provider with the business is essential for seamless business operations.
What is a Payment Gateway?
The term payment gateway refers to software that transmits the payment information between the online website and the bank of the customer or merchant, managing online transactions. It encrypts financial data for the convenient working of payment. The payment gateway can facilitate credit/debit cards, net banking, UPI, digital wallets, etc. For all those essential processes, they integrate payment gateways online and avail safe and efficient e-commerce transactions. Secure online payment gateways should be chosen by every business for their websites to prevent fraud from taking place and to develop customer confidence. Popular choices in the world of payment gateways are PayPal, Razorpay, Stripe, PayU, and EnKash.
Why Does Choosing the Right Payment Gateway Matter?
Selecting a suitable payment gateway is, quite simply, to them regarding transaction processing: it impacts security, customer satisfaction, and, in the end, the business itself. Here’s why it’s important to choose the right payment gateway integration:
1. Ensure the Security of the Transaction
- Secures customer-sensitive data against theft through encryption technologies such as SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security).
- Compliance with PCI DSS standards for preventing data breaches and fraud at payment terminals.
- Fraud prevention mechanisms include 3D Secure authentication, AI-analysed fraud data, and chargeback protection.
2. Increase Customer Satisfaction
- A fast and reliable payment gateway reduces friction at checkout and minimizes abandoned transactions. Supports various payment modes, i.e. credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and UPI, to enable consumers to choose the mode of payment most convenient for them.
- Integrated synchronized user experience with the payment gateway on websites, mobile apps, or e-commerce platforms.
3. Impacts on Business Expansion
- An appropriate payment gateway provider coupled with inter-currency payment functionally established cross-border transactions enables global growth for a business.
- Recurring billing and subscription management are vital for businesses that base their income on subscriptions from customers.
- Provides real-time transaction tracking and analytics which enable businesses to base financial decisions on hard data as opposed to guesswork.
4. Cut costs in payment processing
- Each payment gateway has its field of costs, including transaction fees, set-up fees, refunds, and chargeback fees.
- Costwise, payment gateway comparisons save businesses from the misery of going through unhelpful costly gateways.
- Some payment gateway providers offer a flexible pricing model that could include flat-rate pricing, interchange-plus pricing, or tiered pricing which helps the company to better optimize the costs depending on its volume of transactions.
How Payment Gateways Work?
It is the function of a payment gateway to provide these routines and allow the flow of transactions to be smooth and secure. They connect customers, merchants, acquiring banks, and issuing banks as a facilitator of moving funds from one account to another. The entire process takes only a few seconds, but it is carried out in a structured sequence that ensures a safe and successful transaction.
Step-by-Step Process of Payment Gateway Functioning
1. Customer Initiates Payment
The customer selects a product or service on the merchant’s website or mobile app and proceeds to checkout.
They enter their payment details, such as:
- Credit or debit card information (Card number, CVV, expiration date).
- UPI ID or digital wallet credentials.
- Net banking details for direct transfers.
- Once submitted, the payment request is forwarded to the payment gateway provider.
2. Data Encryption & Authorization
The payment gateway first ensures that the customer’s sensitive payment details are encrypted using SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption so as not to allow data theft. This encrypted payment data is then sent to the merchant’s acquiring bank, which processes the transaction request based on the criteria established. The acquiring bank forwards the details to the customer’s bank, the issuing bank, for verification.
3. Approval and Rejection of Transactions
After the customer has put the funds into their account, the issuing bank checks:
- Whether the amount available at the moment is sufficient or there is enough credit limit available;
- If they suspect the transaction is fraudulent;
- Whether proper security measures have been followed for that payment request (e.g., OTP authentication, 3D Secure verification).
- In this manner, the bank either approves or refuses the transaction.
4. Merchant is not Forfeited
The response by the issuing bank (whether approved or declined) is sent back to the merchant’s website via the payment gateway. If approved, a success notification is sent to the merchant, and the customer receives a confirmation notification. If denied, the transaction is canceled, and the customer is instructed to find an alternate payment method or try again.
5. Settlement Payment
The approved payment is processed, and the money is transferred from the customer’s bank account into that of the merchant. This process can take a few minutes to several business days, depending on the policies of the payment gateway provider and the bank.
Types of Payment Gateways
Based on their operational needs, technical capacities, and customer requirements, shops can select payment gateway providers from a variety of options. Each type has its specific advantages tailored for various business models.
1. Hosted Payment Gateway
A hosted payment gateway directs users to an external page where they can make their payments. After payment, users are returned to the merchant’s website.
How does it work?
Redirect customers to a third-party payment page where they complete the transaction.
After finishing the payment, the customers will be redirected to the merchant’s website.
Pros:
- Easy and quick integration.
- Highly secure, as the payment gateway provider takes care of encryption and compliance.
Cons:
- Can negatively affect user experience since customers leave the merchant website to complete payments.
- Limited branding customization scope.
Examples: PayPal, PayU, Stripe Checkout.
2. Self-Hosted Payment Gateway
A self-hosted payment gateway allows customers to key in payment details right at the merchant’s website. The provided data is then sent securely to the payment processor.
How does it work?
The customers enter their own payment information directly on the merchant’s website, and the payment info is sent to the payment processor securely.
Pros:
- Gives the business better control over branding and predominant user experience.
- Reduces the chance of drop-offs by completing transactions within the business website.
Cons:
- Requires a higher degree of PCI DSS compliance handling and data security from the side of the business.
- Requires a little more complicated payment gateway integration work compared to the hosted solution.
Examples: Razorpay, CCAvenue.
3. API-Based Payment Gateway
Use an API-based payment gateway to integrate it directly with your website or mobile app. It uses a payment gateway API, so it offers the full control you want over the checkout experience.
How does it work?
Integrates directly into the business website or mobile app using payment gateway APIs.
The grantee has full control over the payment process, user interface, and transaction flow.
Pros:
- Highly customizable, which enables businesses to create unique experiences for the checkout.
- Best suited for large-scale e-commerce platforms, FinTech services, and subscription-based models.
Cons:
- Demands advanced technical expertise for API integration and maintenance.
- Businesses that utilize this option must make sure they will comply with the stipulated security standards.
Examples: Authorize.Net, Adyen.
4. High-Risk Payment Gateway
A high-risk payment gateway is defined as a payment gateway specialized in dealing with high-prone fraud and chargeback industries, for example, adult service, gaming, and forex trading. These gateways have certain specialized security measures.
How does it work?
An entity that processes high-risk businesses, such as the following:
- Online gaming and casinos.
- Forex trading and cryptos.
- Adult entertainment and services.
- Special features of fraud protection and chargeback management may apply.
Pros:
- Extra layers of protection to the industries that face a bigger fraud risk.
- Aid high-risk businesses to access processing services that standard gateways might decline.
Cons:
- Increased payment gateway fees are charged owing to increased security risks.
- Some providers may provide high-risk payment processing with tough regulations and compliance arrangements.
Examples include PayKings, Instabill, and high-risk PayPal alternatives.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway provider is crucial for ensuring secure, seamless, and cost-effective transactions. Since payment gateways directly impact customer experience, transaction security, and business revenue, businesses must carefully evaluate different providers based on their features, costs, and reliability.
Here are the key factors to consider when choosing a payment gateway:
1. Security Features – Keeping Transactions Safe
How the payment gateway becomes even more substantial concerning online payment processes would be the customer trusting their sensitive financial information to this business. An ideal gateway for payments should encompass these security measures:
PCI DSS Compliance:
The PCI DSS is the worldwide security standard, assuring that companies enforce best practices for securing cardholder data. Any PCI DSS-compliant payment gateway would help secure against data breaches, fraudulent activities, and associated penalties.
Fraud Detection and Risk Analysis:
A worthy payment gateway provider would have fraud detection tools, like: 3D Secure authentication (OTP verification for card payments), AI-based fraud detection, and Geolocation tracking to trigger alerts for payments coming from high-risk areas.
SSL Encryption and Tokenization:
Secure Socket Layer encryption provides a way and peace of mind for ensuring that any payment data transmitted from customers is encrypted and therefore does nothing to cyber threats. By tokenizing information, sensitive card information is replaced by unique tokens, resulting in a lesser risk of leakage of information that can lead to fraudulent activities in the future. A secure payment gateway will see a customer and merchant alike protected from risks like identity theft, chargeback fraud, or unauthorized transactions.
2. Payment Gateway Fees – Becoming Aware of Costs
Different payment gateways apply different pricing structures, therefore, businesses must account for the total cost of payment processing that best fits their budget. Payment gateways usually charge these fees:
Transaction Fees:
Most providers charge a fee for each transaction, usually a set percentage of the payment amount, e.g., 2.5% + ₹3 per transaction. Some, however, charge flat fees per transaction, which is advantageous for high-value payments.
Setup and Monthly Subscription Fees:
Some payment gateways require one-time setup fees, whereas some do offer free setup. An additional fee, if they apply, usually apply for the monthly subscriptions of those enhanced features that include fraud prevention, multi-currency support, and analytics tools.
Chargeback and Refund Fees:
If the customer wants a transaction to be disputed, a chargeback fee can be applied. Some charge a further fee for handling refunds, adding to the expenses incurred by any organization.
Currency Conversion Fees:
These should be looked into when the businesses rendering either internal or international payment procedures will be accepting payments.
Comparison of Payment Gateway Costs:
Thus, the business shall compare different payment gateways based on their charging criteria and arrive at one such option that best suits the business in terms of price while giving the most essential features.
3. Supported Payment Methods – Customer-Driven
The more flexible the payment gateway is in terms of acceptable payment methods, the greater the likelihood that the customers can pay the way they want. The more options there are, the more likely conversion and retention are.
Credit/Debit Card Payments:
The gateway should support the major cards: Visa, MasterCard, American Express (AMEX), RuPay, and Discover.
UPI, Net Banking, and Digital Wallets:
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has enjoyed wide acceptance in India and should be supported.
- Net Banking facilitates payment directly from the bank account of the customer.
- Digital wallets like Google Pay, Paytm, PhonePe, Apple Pay, and Samsung Pay ensure that payments are made swiftly and securely.
EMI and BNPL:
- EMI (Equated Monthly Installments), as a way of supporting customers, becomes a comfortable means for high-value purchases in any case.
- BNPL services work for anyone interested in purchasing an item.
International Payment Support:
For all businesses working internationally, the acceptance of the payment gateway must support:
- Multi-currency payments for international trades.
- Need to plug in international payment methods like PayPal, Stripe, and Wise.
- Choosing a payment gateway that could support a large variety of payment methods would enhance sales conversions, customer satisfaction, and business growth.
4. Easy Integration – Seamless Setup and Use
A payment gateway should be easy to integrate with any website, mobile application, or e-commerce platform without the need for complex coding or deeper technical expertise.
API & SDK Support:
The payment gateway should offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and SDKs (Software Development Kits) to:
- Allow custom payment gateway integration in business websites and apps.
- Allow for excellent checkout experiences for customers.
E-Commerce Platform Compatibility:
As in the case of e-commerce platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, and BigCommerce, the business should opt for a gateway with plugins readily available for quick integration.
Minimal Technical Setup:
The payment gateway provider should provide documentation, along with tutorials and support from developers, that gives the most, if not far, in terms of easy setup. A few providers may also have no-code solutions that let a business start receiving payments without any significant heavy development work. A user-friendly payment gateway with simple integration options ensures a smooth payment process for both merchants and customers.
5. Customer Support – Resolve Issues Fast
Reliable customer support is essential to rectify payment failures, technical glitches, or disputes about transaction matters. In this respect, businesses need to consider the following:
24/7 Availability:
A payment gateway provider should provide support 24/7, especially for international businesses with sundry time zones.
Multiple Support Channels:
These should include live chat, email, and phone support so you can quickly fix any payment-related issues.
Resolution Timeline and Response Time for Issue Quelling:
Comments and ratings by customers regarding how promptly the provider solves technical issues and transaction problems. Good customer support ensures that payment issues get solved quickly, leading to reduced downtimes and enhanced customer faith.
6. Global Reach – Businesses Going Worldwide
If a business is anticipated to go worldwide, it must ensure that the payment gateway would allow cross-border transactions and payments in multiple currencies.
Multi-Currency Support:
The gateway should allow customers to make payments in their local currency with live currency conversion.
Cross-Border Payment Capabilities:
Companies should also verify the existence of low international transaction fees and support from multiple banking networks worldwide.
Compliance with International Regulations:
Each country has its unique financial regulations, and a business must choose a gateway that complies with:
- GDPR for Europe,
- PSD2 (Revised Payment Services Directive)-for EU transactions,
- RBI Guidelines for Indian payment processors.
Global Integration of Payment Methods:
Support for international payment systems, such as PayPal, Alipay, Wechat Pay, and Western Union, pull in international customers for a business. A payment gateway with global capabilities allows a business to scale up internationally and get more revenue potential.
Payment Gateway Comparison
Choosing the best payment gateway requires analyzing various factors, such as ease of integration, security, transaction fees, and global accessibility. Below is a detailed comparison of some top payment gateway providers to help businesses make an informed decision:
Payment Gateway |
Ease of Integration |
Transaction fees |
Security features |
Global Support |
EnKash |
User-friendly – A complete corporate expenditure management solution with easy interfaces. |
Competitive – Economical solutions for business enterprises. |
Robust – Highly secure, supported by advanced features including PCI DSS compliance. |
Growing – An ever-growing presence extending beyond India. |
PayPal |
Simple setup with multiple plugins and APIs. |
High Transaction and currency conversion fees |
Strong – PCI DSS compliance followed; fraud detection and encryption |
Well, Present in 200-plus countries. |
Stripe |
API-based installation would be required to be fairly moderate, hence its developer suitability |
Moderate- Great, transparent pricing with volume discounts |
Strong- Advanced fraud detection and security protocols |
Supported- Yes, for international transactions |
Razorpay |
Simple – Smooth integration with Indian e-commerce systems |
Cheaper – Competitive pricing for domestic transactions |
Very secure – PCI DSS Level 1 certification and fraud protection |
No – Routing mainly in India |
PayU |
Medium – Technology platform API-based and plugin-based integration for multiple platforms. |
Lower – Cheap domestic payments. |
High – Encryption, anti-fraud tools. |
Limited – Supports selected countries other than India. |
Also read: What and How of Merchant Payment Gateway
Merchant Account vs. Payment Gateway
Many businesses get confused between a merchant account and a payment gateway, assuming they serve the same purpose. However, they play different roles in payment processing.
Feature |
Merchant Account |
Payment Gateway |
Purpose |
A special kind of bank account that holds temporary funds before transferring them to a business account. |
Online services that process and authorize customer payments. |
Function |
Acts as an intermediary between a business and the bank. |
They function as an intermediary between the customer, merchant, and payment processor. |
Requirement |
Required to receive credit/debit card payments directly. |
Authorization, encryption, and transaction completion are applied to the payment transaction. |
Transaction Processing |
Transfers funds from sales after a holding period into the business account. |
Approve or decline the transaction in real-time based on security checks. |
Example Services |
Business banks are provided by financial institutions. |
PayPal, Stripe, Razorpay, PayU, and Authorize.Net |
Conclusion
Choosing the right payment gateway is essential for secure payment processing, customer credibility, and business growth. The comparison between transaction fees, setup costs, and refund policies would help businesses optimize their expenses before locking into contracts. The correct integration into websites, mobile applications, and e-commerce platforms is necessary for a smooth user experience. An array of security features such as PCI DSS, SSL encryption, and Fraud Detection would safeguard sensitive information. Multiple payment modes would also be an added convenience for the customer and a global reach. A payment gateway that is well-matched eliminates payment failures, increases conversion, and provides financial security. Careful evaluation and prioritization of security leads to a profitable, hassle-free payment system.