In today’s fast-paced digital world, traditional paper-based processes are being replaced by more efficient and streamlined electronic methods. The introduction of electronic payments and e-invoicing under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India is a significant step toward modernizing tax compliance and business operations. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of e-invoicing under GST, its applicability, benefits, and much more.
Introduction
The implementation of GST in India in 2017 marked a major shift in the country’s indirect tax regime. GST aimed to simplify taxation by replacing a multitude of state and central taxes with a unified tax structure. In this pursuit of simplification and modernization, e-invoicing emerged as a crucial component.
E-invoicing, or electronic invoicing, refers to the generation and exchange of invoices in a standardized digital format, ensuring the authenticity of the document. It simplifies the invoice generation process and enhances tax compliance by reducing errors and promoting transparency.
Latest Updates
August 1, 2023 – According to Notification 10/2023-Central Tax, businesses with more than Rs 5 crore turnover will have to issue e-invoices w.e.f from August 1.
June 12th, 2023 – From July 15, 2023, NIC has instructed Two-factor Authentication for business owners with more than Rs 100 crore turnover. This will be applicable for e-invoicing and e-way billing.
June 9th, 2023 – The GSTIN has launched a user-friendly ‘e-invoice QR code verifier’ app on Google Play Store for convenient e-invoice verification. It authenticates QR code information. The iOS version will be available shortly.
May 10, 2023 – CBIC has announced the sixth phase of e-invoicing. Businesses with more than Rs 5 crore turnover since 2017-18 will have to issue invoices starting from August 1, 2023.
May 6th, 2023 – The Department of GST has extended the 7-day time limit of reporting old e-invoices on the e-invoice IRP portals to three months. The department will announce the new implementation date.
April 13, 2023 – According to the GST Network advisories on April 12th and 13th, taxpayers with an annual turnover of Rs 100 crore or more will have to report tax invoices and credit-debit notes to IRP within a week of invoice date from May 1st, 2023.
January 30, 2023 – NIC e-invoice latest updates:
- Users can choose ’96-Other Country’ as POS state code for items with HSN codes 9965 and 9968.
- Documents dated 1/10/2021 or later are now valid on the portal.
- A new error code 2295 for duplicate requests has been added, in addition to 2150, indicating ‘IRN is already generated and registered with GSTN Lookup Portal by other IRP.’
Also Read: GST State Code List
What is E-Invoicing Under GST?
E-invoicing under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India is a transformative approach to invoice generation and reporting that harnesses the power of digital technology. It marks a significant departure from the traditional paper-based invoicing system that prevailed before the introduction of GST in 2017. E-invoicing, short for electronic invoicing, is essentially the creation and exchange of invoices in a standardized digital format, ensuring the authenticity and accuracy of these documents.
The primary objective of E-Invoicing is to streamline and modernize the entire invoicing process, from creation to reporting. It leverages advanced digital infrastructure to simplify compliance, minimize errors, promote transparency, and curb tax evasion. Under this system, businesses generate invoices electronically and transmit them directly to a specialized platform known as the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
The IRP plays a pivotal role in E-Invoicing by validating the invoices and assigning each one a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN). This ensures that each invoice is officially recognized and cannot be easily tampered with. Once the IRP authenticates and approves the invoice, it is then sent to the recipient. This entire process occurs in real time, allowing tax authorities to access crucial transaction data promptly.
Who Must Generate an E-Invoice and Its Applicability?
The applicability of e-invoicing is determined based on the turnover of the taxpayer. As of August 2023, the e-invoice threshold limit was set at INR 5+ crore for aggregate turnover. Businesses exceeding this threshold are mandated to generate e-invoices for their transactions.
Also read: Types of GST
Transactions and Documents Criteria
Under GST e-invoicing, the following types of transactions and documents are covered:
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Transactions: E-invoicing is mandatory for all B2B transactions, regardless of the invoice value.
- Export Invoices: All invoices issued for export transactions are subject to e-invoicing.
- Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM): If the recipient is liable to pay tax under the RCM, e-invoicing is required.
- Credit and Debit Notes: Any credit notes in GST or debit notes related to B2B transactions are also covered under e-invoicing.
- Invoice Reference: Any document that references an invoice, such as delivery challans and bill of supply, should also be reported to the IRP.
Please note that the applicability criteria and thresholds may be subject to changes by the GST Council. It’s advisable to refer to the latest notifications and updates on the GST portal or consult a tax expert for the most current information.
Automate invoices without any hassle
Book A Demo Now
Automate invoices without any hassle
Book A Demo Now
Who Need Not Comply with E-Invoicing?
While e-invoicing is mandatory for businesses above the specified turnover threshold, certain categories of taxpayers are exempt from compliance. These include
- SEZ Units (Special Economic Zone Units): SEZ units are among the entities that are exempt from E-Invoicing requirements. Special Economic Zones are designated areas in India that are deemed to be outside India’s customs territory for trade operations and duties. Businesses operating within SEZs enjoy various tax benefits and incentives. While SEZ units are exempt from E-Invoicing, they are still subject to other GST compliance procedures, such as filing types of GST returns.
- Insurance Companies: Insurance companies, which provide a wide range of coverage, including life insurance, health insurance, and property insurance, are another category that is not mandated to comply with E-Invoicing. However, they are required to adhere to other GST compliance requirements, such as filing accurate GST returns.
- Banking Companies and Financial Institutions: Banking companies and financial institutions, including banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial intermediaries, are also exempt from E-Invoicing obligations. These entities are responsible for various financial services, including lending, deposit-taking, and investment activities. While they are not required to generate E-Invoices, they must still adhere to other aspects of GST payment compliance, including the accurate filing of GST returns.
- Small and Micro Enterprises (SMEs): Although not explicitly mentioned in the initial list, small and micro enterprises with turnover below the specified threshold are generally not subject to E-Invoicing requirements. These businesses often operate with limited resources and may not have the infrastructure in place to generate E-Invoices electronically. However, they are still expected to comply with other GST regulations relevant to their operations.
- Agricultural and Primary Produce Traders: Certain businesses involved in the trading of agricultural and primary produce may also be exempt from E-Invoicing, especially if their turnover is below the threshold specified by the GST Council. These businesses typically deal with goods like grains, vegetables, and fruits and may operate in local or rural markets.
- Government Departments and Bodies: Government departments and bodies, including central and state government agencies, are generally exempt from E-Invoicing requirements. They follow their own invoicing and accounting procedures, which are separate from those of private enterprises. However, they are subject to their own set of financial regulations and reporting requirements.
It’s important to keep in mind that even though these categories are exempt from e-invoicing, they are still required to follow other GST compliance procedures.
Systems Before & After E-Invoicing
Before the introduction of e-invoicing, businesses relied on manual methods for invoice generation and submission. This often led to errors, delays, and increased compliance challenges. With the implementation of e-invoicing, the process has become much more streamlined and efficient.
Systems Before E-Invoicing
Before e-invoicing, the typical process involved the following steps:
- Manual Invoice Generation: Businesses would manually generate invoices using accounting software or handwritten ones.
- Data Entry: Data from invoices had to be manually entered into the GST portal for tax compliance.
- Paperwork: Physical copies of invoices and supporting documents were often maintained, leading to storage and retrieval challenges.
- Tax Filing: Businesses had to manually reconcile data and file GST returns, which could be time-consuming.
Systems After E-Invoicing
With e-invoicing, the process has become more automated and efficient:
- Electronic Invoice Generation: Invoices are generated electronically, often directly from accounting software or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems.
- Real-time Reporting: Invoices are reported to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) in real time, reducing the chances of errors and fraud.
- Instant Verification: The IRP validates invoices instantly and assigns unique IRNs, assuring authenticity.
- Reduced Compliance Burden: E-invoicing simplifies GST return filing as data is automatically populated in the return forms.
- Storage and Retrieval: Digital copies of invoices can be easily stored and retrieved, reducing paperwork.
Time Limit to Generate E-Invoice
Taxpayers are required to generate an e-invoice in real-time at the time of issuing an invoice to the recipient. There is no specific time limit for generating an e-invoice other than the requirement that it must be done at the time of invoice creation. The invoice data is then transmitted to the IRP for validation and generation of the IRN.
Process of Getting an E-Invoice
The process of getting an e-invoice involves several steps:
- Invoice Generation: Create the invoice using accounting software or an ERP system. The invoice should contain all mandatory details as per GST rules.
- Upload to IRP: Upload the invoice data to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). This portal will validate the data and generate an IRN.
- IRN Generation: The IRP will validate the invoice and generate a unique IRN along with a QR code.
- Sending to Recipient: Send the e-invoice, including the IRN and QR code, to the recipient.
- GST Return Filing: The data from the e-invoice is automatically populated in your GST return forms, simplifying the return filing process.
Benefits of E-Invoicing to Businesses
E-invoicing offers a wide range of benefits to businesses, both large and small:
- Reduced Errors: E-invoicing significantly reduces the likelihood of errors in invoice data. Manual data entry errors, such as typos and miscalculations, are minimized when invoices are generated electronically. This reduction in errors helps businesses avoid compliance issues, potential penalties, and the need for time-consuming corrections.
- Enhanced Efficiency: The automation of the invoicing process through E-Invoicing leads to improved operational efficiency. Businesses can save valuable time and resources that would have otherwise been spent on manual data entry, verification, and reconciliation. This efficiency boost allows organizations to focus on core business operations, innovation, and growth strategies.
- Faster Payments: E-Invoices are processed faster compared to traditional paper invoices. Quick and accurate invoicing leads to shorter payment cycles. As a result, businesses can expect improved cash flow, which is crucial for managing working capital, meeting financial obligations, and seizing growth opportunities.
- Real-time Compliance: E-Invoicing enables real-time reporting of transactions to the GST portal. This means that businesses are always up to date with their tax compliance. The instantaneous transmission of data ensures that there are no delays or lapses in reporting, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
- Reduced Tax Evasion: E-invoicing plays a pivotal role in minimizing the chances of tax evasion and fraudulent activities. All transactions are electronically tracked and reported in real-time. Tax authorities can easily cross-verify input and output tax credits, ensuring that businesses are not falsely claiming credits. This transparency and accountability discourage tax evasion and fraud.
- Digital Record Keeping: E-Invoicing facilitates digital record keeping, reducing the reliance on physical paperwork. Electronic copies of invoices and related documents can be easily stored, organized, and retrieved as needed. This saves physical storage space and streamlines record-keeping processes, making audits and compliance checks more efficient.
- Simplified GST Return Filing: One of the most significant advantages of E-Invoicing is the automatic population of data in GST return forms. E-invoice data seamlessly flows into the relevant sections of GST returns, reducing the manual effort required for return filing. This simplification of the return filing process leads to greater accuracy and timeliness in fulfilling tax obligations.
- Enhanced Vendor-Customer Relationships: E-invoicing also benefits relationships between vendors and customers. The streamlined invoicing process and reduced errors mean fewer disputes and discrepancies. This, in turn, fosters trust and collaboration between business partners, contributing to long-term relationships and mutual growth.
- Cost Savings: E-invoicing can lead to significant cost savings over time. Savings are realized through reduced printing and postage costs associated with paper invoices, decreased manual labor, lower error correction expenses, and streamlined processes. These cost savings can positively impact a business’s bottom line.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing the need for paper invoices and physical storage, E-Invoicing aligns with sustainability initiatives. It contributes to environmental conservation by reducing paper consumption and the associated environmental footprint.
How Can E-Invoicing Curb Tax Evasion?
E-invoicing plays a crucial role in curbing tax evasion by introducing transparency and accountability into the taxation system. Here’s how it helps:
- Real-time Reporting: E-invoicing ensures that all B2B transactions are reported in real-time to the GST portal, leaving no room for manipulation.
- Invoice Authentication: The IRP validates invoices and assigns unique IRNs, confirming the authenticity of the documents.
- Matching Input and Output Tax: Tax authorities can easily match the input tax credit claimed by buyers with the output tax paid by suppliers, minimizing the risk of false claims.
- Reduced Manual Intervention: Automation reduces the need for manual data entry, which is often prone to errors and manipulation.
- Audit Trail: E-invoicing creates a digital audit trail, making it easier for tax authorities to track transactions and identify discrepancies.
- QR Code Verification: The inclusion of a QR code on e-invoices allows tax authorities and buyers to verify invoice details quickly.
E-invoicing is a powerful tool for tax authorities to ensure tax compliance and prevent tax evasion.
What Are the Required Fields of an E-Invoice?
An e-invoice under GST must contain certain mandatory fields to be considered valid. These fields include:
- GSTIN: The Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) of the supplier and the recipient.
- Invoice Number and Date: A unique invoice number and the date of issuance is required.
- Invoice Value: The total invoice value, including the tax amount.
- HSN Code: The Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) code of the goods or services supplied.
- Place of Supply: The location where the goods or services were supplied.
- Description of Goods/Services: A detailed description of the goods or services provided.
- Quantity and Unit: The quantity of goods or services and the unit of measurement.
- Taxable Value and Tax Amount: The taxable value of the goods or services and the applicable GST rates.
- Reverse Charge: If applicable, whether the reverse charge mechanism is applicable.
- Signature: The supplier’s or authorized person’s Digital or electronic signature.
- QR Code: A Quick Response (QR) code containing invoice details for quick verification.
Businesses must ensure that all these mandatory fields are correctly filled out in their e-invoices to avoid compliance issues.
What Does the E-Invoice Look Like?
An e-invoice under GST follows a standardized format, which includes the mandatory fields mentioned earlier. Here’s an example of what an e-invoice might look like:
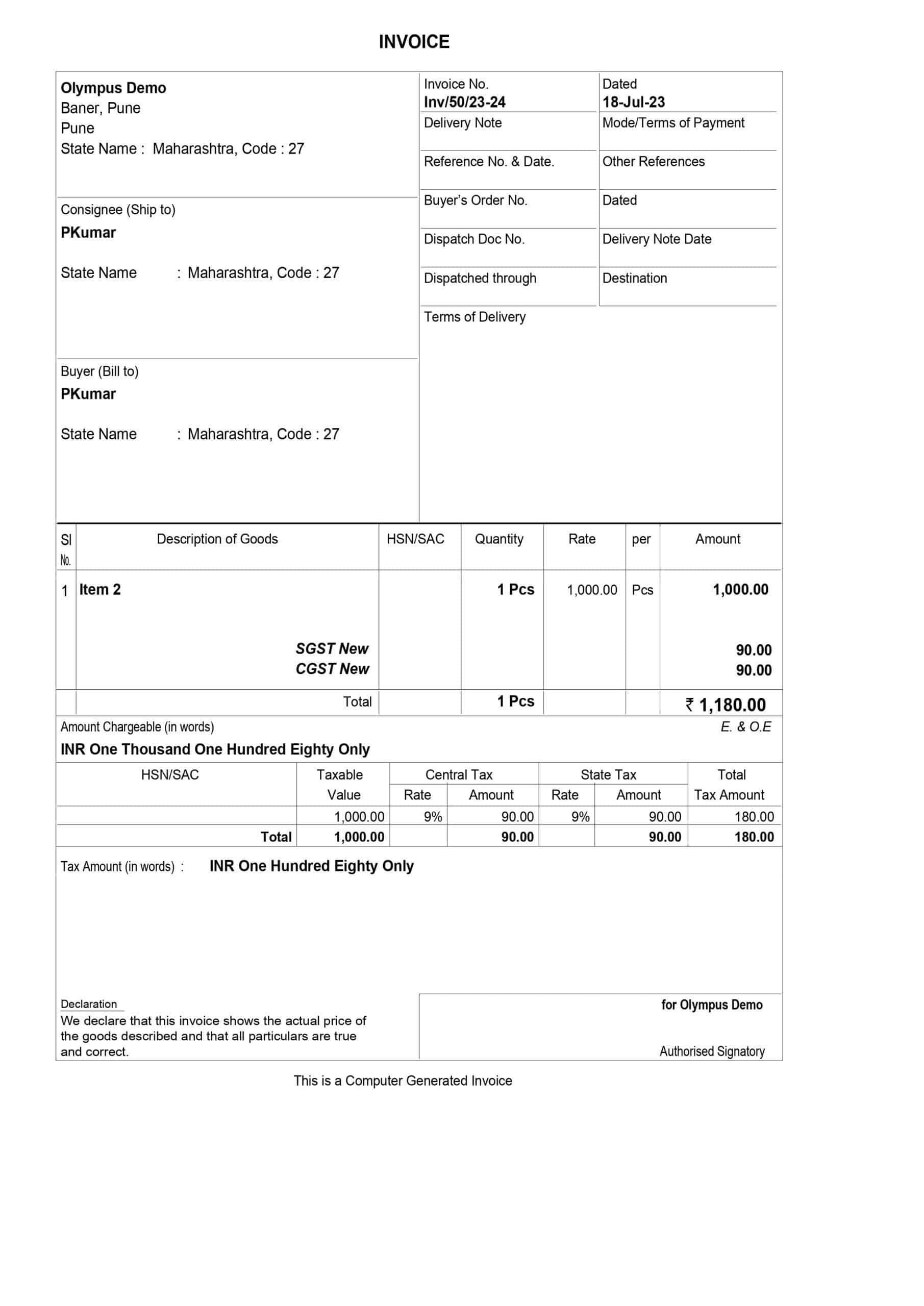 What Are the Types of Documents That Are to Be Reported to the IRP?
What Are the Types of Documents That Are to Be Reported to the IRP?
Under the e-invoicing system, various types of documents and transactions are reported to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). These include:
- Tax Invoices: These are the primary documents issued by suppliers to recipients for the supply of goods or services.
- Credit Notes: Credit notes are issued by suppliers to recipients when there is a reduction in the invoice value, such as for returns or discounts.
- Debit Notes: Debit notes are issued by suppliers to recipients when there is an increase in the invoice value, such as for additional charges.
- Export Invoices: Invoices issued for export transactions are also reported through e-invoicing.
- Bill of Supply: This document is issued when a registered supplier makes a supply of exempted goods or services.
- Delivery Challans: Documents accompanying the transportation of goods without issuing a tax invoice.
- Other Relevant Documents: Any other documents that reference or pertain to the invoices issued by businesses.
Conclusion
E-invoicing under GST represents a significant leap toward modernizing tax compliance and business operations in India. Digitizing the invoicing process reduces errors and enhances efficiency, and plays a crucial role in curbing tax evasion. While the implementation of e-invoicing may pose initial challenges for businesses, the long-term benefits far outweigh the hurdles. As the GST Council continues to refine and expand the e-invoicing framework, businesses must stay informed about the latest updates and compliance requirements. Embracing e-invoicing is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a strategic move to streamline operations, ensure transparency, and thrive in the digital age of taxation.
EnKash Olympus helps you automate invoices and eliminates the need to manage invoices over mail or in hard copies. As a business, you can use the platform to send the e-invoice to your vendors seamlessly as a part of your accounts payable. You can also use EnKash Olympus for your accounts receivable in order to raise an e-invoice to your customer. This will make it easier for you to keep track of the invoices as you can decide on the workflow as per your convenience. Your customers will receive regular reminders, and this automation will smoothen the AP & AR cycle, keeping the cash flow in check.
Read these FAQs to know more about e-invoicing under GST:
What is e-invoicing under GST, and why was it introduced?
E-invoicing under GST refers to the electronic generation and exchange of invoices in a standardized format. It was introduced to streamline tax compliance, reduce errors, and enhance transparency in the taxation system.
Who is required to generate e-invoices under GST?
Businesses with a turnover exceeding the specified threshold, as determined by the GST Council, are required to generate e-invoices for their transactions.
What are the benefits of e-invoicing to businesses?
E-invoicing offers benefits such as reduced errors, enhanced efficiency, faster payments, real-time compliance, and simplified GST return filing.
How does e-invoicing help in curbing tax evasion?
E-invoicing curbs tax evasion by enabling real-time reporting, invoice authentication, input-output tax matching, and digital audit trails, making tax evasion difficult.
What are the mandatory fields in an e-invoice under GST?
Mandatory fields in an e-invoice include GSTIN, invoice number and date, invoice value, HSN code, place of supply, description of goods/services, quantity and unit, taxable value and tax amount, reverse charge, signature, and QR code.
What is the process of generating an e-invoice under GST?
The process involves invoice generation, uploading to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), IRN generation, sending the e-invoice to the recipient, and automatic population of data in GST return forms.
Is e-invoicing applicable to all types of businesses?
E-invoicing is primarily applicable to B2B transactions, export invoices, reverse charge mechanisms, credit and debit notes, and other documents referenced in invoices. Certain categories of businesses, like SEZ units and insurance companies, are exempt.
What does an e-invoice look like, and is there a standardized format?
An e-invoice under GST follows a standardized format, including mandatory fields. It typically contains details like GSTIN, invoice number, invoice value, HSN code, and more, ensuring consistency and clarity.
Is there a time limit for generating an e-invoice?
E-invoices must be generated in real time at the time of issuing an invoice to the recipient. There is no specific time limit other than this requirement.
When was e-invoicing introduced, and what is the timeline for its implementation?
E-invoicing was introduced in India in a phased manner, starting with businesses with a turnover exceeding INR 500 crore. As of August 2023, the e-invoice threshold limit was set at INR 5+ crore for aggregate turnover. Businesses exceeding this threshold are mandated to generate e-invoices for their transactions.













